Relying on your developers to build and maintain integrations via custom code (i.e., point-to-point integrations) isn’t sustainable.
Your engineers must modify and troubleshoot the integrations over time. Your organization becomes vulnerable when these developers leave, as they may take their knowledge of the integrations they built with them. Depending on the size of your tech stack, your developers must implement and manage anywhere from dozens to hundreds of point-to-point integrations.
To help avoid these issues, you can turn to a third-party integration solution.
We’ll highlight the different categories of tools you should be aware of, as well as some of the features to look for during your evaluation. But first, let’s align on what an integration solution is.
What Is an Integration Solution?
An integration solution is a third-party system that enables businesses to establish, manage, and maintain connections between various cloud applications, on-premise systems, or hybrid environments. It serves as a bridge, allowing data and functionality to flow seamlessly between otherwise siloed systems. You can deliver these solutions in the cloud, on-premises, or as a hybrid. It depends on the provider and business requirements.

Why Are Integration Solutions Important?
Integration solutions are essential for several reasons:
- Streamlining Business Operations: An integration solution connects disparate applications and ensures data flows smoothly across systems, reducing redundancy and improving operational efficiency. This results in better coordination and alignment across departments.
- Enhancing Agility: Organizations can adapt more readily to changing business needs by using integration solutions. Instead of building custom, point-to-point connections, which are labor-intensive and difficult to scale, integration solutions offer a flexible approach that enables rapid reconfiguration and extension.
- Reducing IT Overhead: Relying on custom integrations can strain development teams who are tasked with building and maintaining each connection. Integration solutions, particularly those with low-code/no-code capabilities, allow non-technical users to create integrations, thus freeing up IT resources for more strategic tasks.
- Improving Data Accuracy and Access: With an integration solution, data across applications is kept consistent, reducing errors and enabling teams to make better-informed decisions based on unified data.
- Supporting Compliance and Security: Comprehensive integration platforms often come equipped with governance and security features that protect data privacy and help organizations comply with regulations like GDPR.
Related: What is application integration?
Benefits of an Integration Solution
An integration solution provides essential advantages, helping organizations operate more effectively, efficiently, and securely. Here are some of the primary benefits:
- Increased Operational Efficiency: Integration solutions automate the flow of data across systems, eliminating manual processes and reducing the risk of human error. As a result, teams can focus on higher-value tasks. Additionally, automation ensures data consistency across all integrated applications, which is critical for real-time insights and decision-making.
- Enhanced Scalability: As organizations grow, so does the complexity of their tech stack. An integration solution can scale with business needs, allowing additional applications to be seamlessly connected without the need for time-consuming custom code. This adaptability is crucial for businesses looking to expand and evolve their operations without being limited by their technology.
- Improved Collaboration: Integration solutions connect different departments’ applications. They therefore break down data silos and encourages cross-functional collaboration. For example, sales, marketing, and support teams can access shared, up-to-date customer information, resulting in more cohesive and informed customer interactions.
- Faster Innovation Cycles: Integration solutions that offer low-code/no-code functionality allow business users to implement and adjust integrations as needed, reducing dependency on IT. This capability accelerates innovation by enabling faster deployment of new processes and applications that respond to market or operational demands.
- Stronger Security and Compliance: Modern integration platforms are designed with robust security and compliance measures. Features like role-based access control, data encryption, and detailed audit logs help protect sensitive information and comply with regulatory requirements, ensuring that integrations don’t introduce vulnerabilities to the organization.
- Cost Savings: Integration solutions centralize and automate integrations. They therefore allow organizations to reduce the ongoing costs associated with building, maintaining, and troubleshooting point-to-point connections. Integration solutions can also reduce the risk of costly data errors and compliance fines, contributing to both direct and indirect savings.
Types of Integration Solutions
Here are a few common categories of integration solutions:
Enterprise Service Bus (ESB)
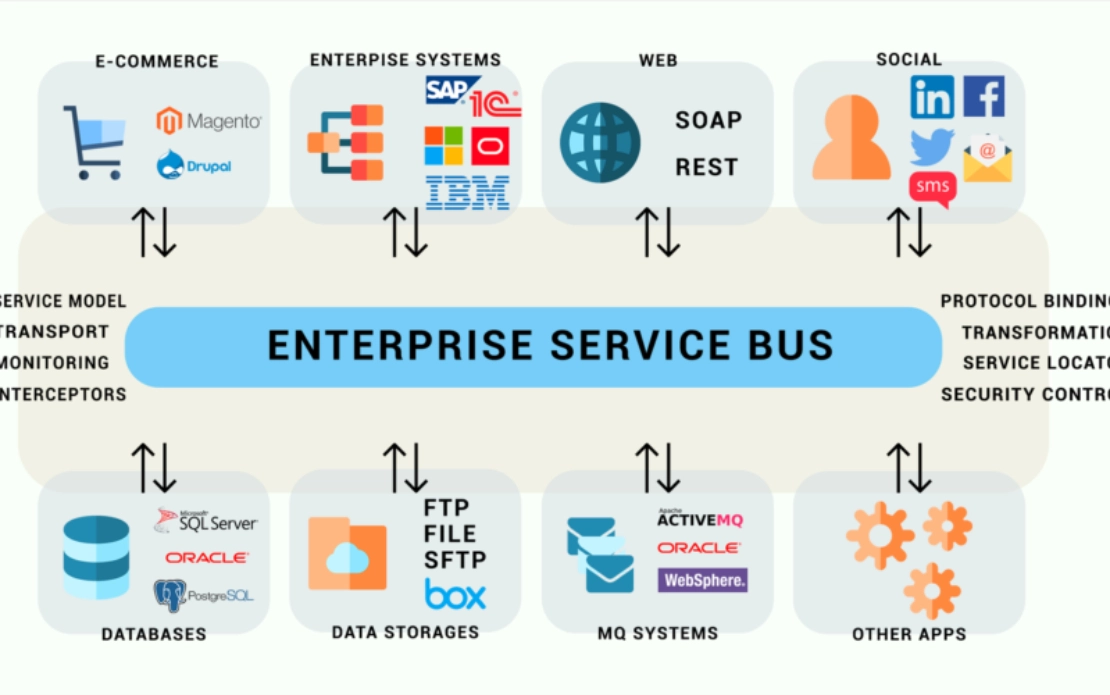
An ESB is an architecture that includes rules and principles for how apps can connect to a “communication bus” middleware. Once an application connects to it, its data can easily flow to the bus, where the data can then be transformed and moved on to other systems that are connected to the bus.
This type of integration tool provides a central location for building, monitoring, and troubleshooting integrations. It also allows you to connect numerous applications to the bus. That said, it requires technical expertise to use, thereby limiting its adoption and scalability at your organization. In addition, if the bus experiences any issues, the applications connected to it are left vulnerable.
Native integrations
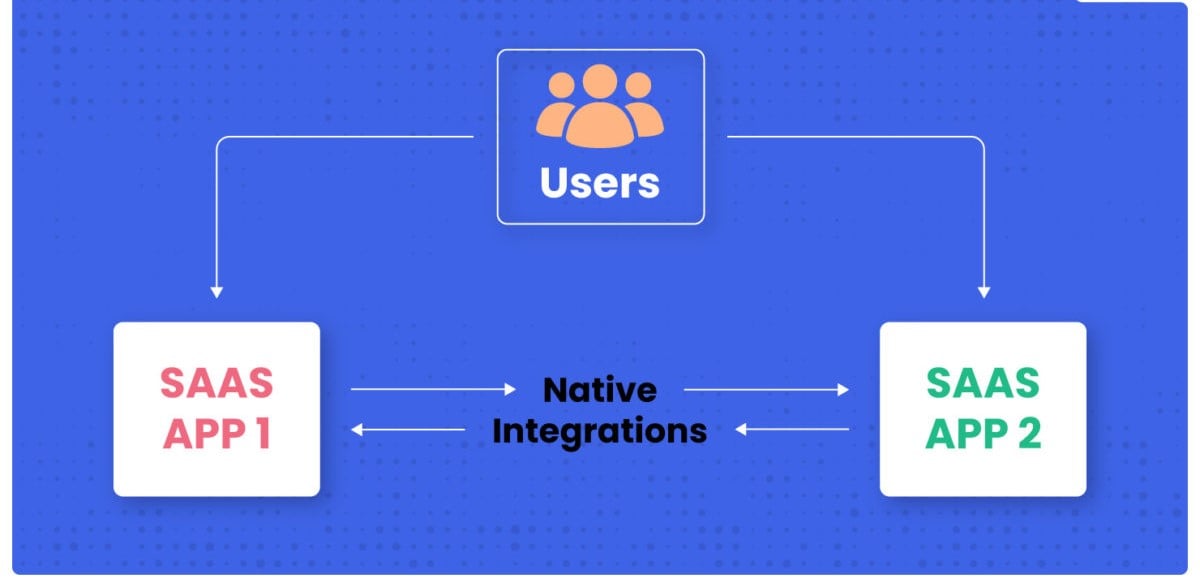
Native integrations are any that a business application (e.g., ERP system) offers. They are likely to come included with your subscription, or at a low additional cost. However, providers often offer a limited number of them. Moreover, given that engineering departments at these organizations face competing priorities, these integrations likely don’t improve at the pace you’d expect, and any issues may not get resolved as quickly as you’d need them to.
Integration Software as a Service (iSaaS)

An iSaaS is a cloud-based, low-code/no-code solution for connecting applications and databases and implementing task automations that work across them.
While iSaaS solutions can be adopted by lines of business, their scope of automation capabilities are inherently limited; for example, they don’t let you automate processes end-to-end. They also likely don’t provide the level of governance and security you need to protect the sensitive, confidential information in your connected applications.
Integration Platform as a Service (iPaaS)
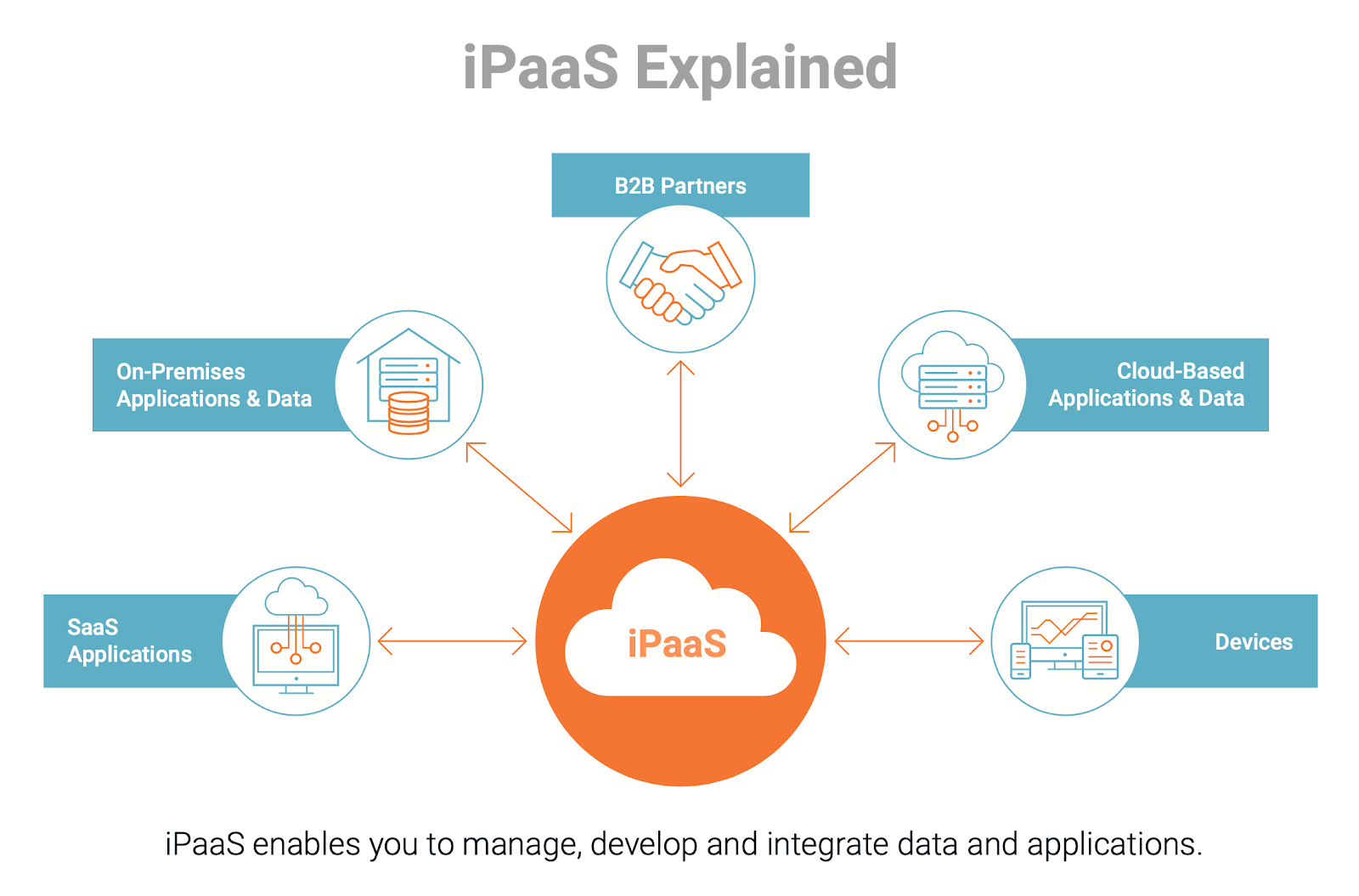
An iPaaS is also cloud-based, and it allows you to connect applications, data, and processes.
A traditional iPaaS often offers powerful governance and security controls, and it likely comes with pre-built connectors to numerous applications and databases. However, it can require technical expertise to use, and it may not address your organization’s automation requirements.
How to Choose an Integration Solution
Selecting the right integration solution depends on your organization’s unique needs, existing tech stack, and long-term goals. Here are some key factors and use cases to consider when evaluating options:
Complexity and Scale of Integration Needs
If your organization has numerous applications across various departments, consider a scalable iPaaS (integration platform as a service). In addition, iPaaS solutions offer robust governance and security controls. Moreover, they include pre-built connectors, making them ideal for enterprises that need efficient management of multiple integrations.
iPaaS solutions are optimal for organizations looking to standardize and secure their integrations across complex or expanding tech environments.
Technical Expertise and Resources
For organizations with limited IT resources, an iSaaS (integration software as a service) offers low-code/no-code functionality.
iSaaS solutions allow business users to set up and adjust integrations independently, making them ideal for smaller teams or businesses that prioritize quick deployment and ease of use over customization.
Data Security and Compliance Requirements
If your organization handles sensitive data, such as in finance or healthcare, choose a solution with strong data governance features.
Look for features like role-based access control and compliance with industry standards.
Enterprise-grade iPaaS solutions often include certifications like SOC 2 and GDPR, along with advanced security settings. These make them ideal for highly regulated industries.
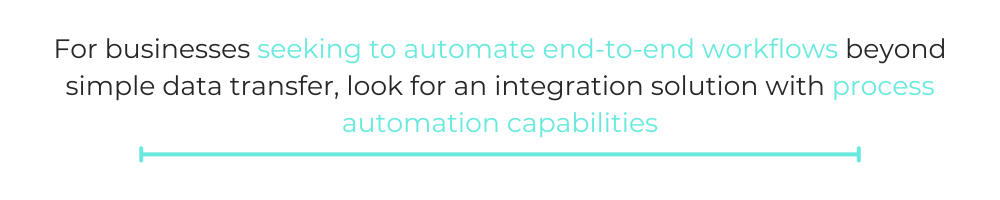
Automation and Workflow Requirements
For businesses seeking to automate end-to-end workflows beyond simple data transfer, look for an integration solution with process automation capabilities.
Additionally, advanced iPaaS platforms can support complex automation needs.
On the other hand, specialized workflow automation solutions or ESBs (enterprise service buses) may be better suited for organizations with specific, well-defined automation goals.
Budget and Cost of Ownership
If budget constraints are a priority, native integrations provided by software vendors can be a cost-effective solution for connecting specific applications.
Native integrations offer basic connections at a low cost, but they may lack the flexibility of third-party platforms. They work well for smaller companies or teams with limited integration needs.
Key Features of an Integration Solution
Given all these categories and their respective pros and cons, the prospect of pinpointing a solution that does the best job of meeting your integration needs can be intimidating. We’ll try to make it less daunting by covering some of the features you should look at more closely during your evaluation.
Comprehensive and Robust Library of Application Connectors
As you evaluate different vendors, you’ll need to learn about the application connectors (pre-built, API-based connections to applications and databases) they currently offer, or will offer soon, and the set of endpoints available for the ones you’re interested in.

Cloud-Native Solution
A platform that’s cloud-native is optimized to connect your SaaS applications. Coupling this with the fact that your level of investment in SaaS technologies has likely increased as of late (and will likely continue to grow over the coming years), the benefits of using a cloud-native solution will only amplify.
Wide-Ranging Functionality
While integration is important, it’s only one part of your digital transformation journey. Your organization should look for a tool that also offers API management capabilities, a process-oriented approach to automation, data integration functionality, platform bots for business communications platforms (e.g., Slack), and more.
Low-Code/No-Code UX
By offering a low-code/no-code UX, you’re allowing business teams to participate in the process of building and maintaining integrations. Aside from freeing up IT and engineering, this allows employees who are well-versed in their department’s business processes and applications to implement more impactful integrations over time.
Related: Tips for empowering citizen automators
Enterprise-Grade Security
As you open your integration platform up to more employees, it’s critical that it provides enterprise-grade governance and security controls. Only then can you prevent (or quickly mitigate) activities that compromise your clients, employees, or your business. With this in mind, look out for features like role-based access control and activity audit logs, and check to make sure that solution is compliant with critical regulations like GDPR and has passed audits like SOC 2 Type 2.
Access All of These Features with Workato
Workato, the leader in enterprise automation, empowers organizations to streamline and scale their integration and automation efforts. As an integration platform as a service (iPaaS), Workato offers over a thousand pre-built connectors. These connectors allow seamless connections between various cloud and on-premise applications.
With a low-code/no-code interface, Workato allows both business users and IT teams to design and deploy complex workflows. As a result, users can do this without deep technical expertise, making the platform accessible across your organization. Integration + Automation + AI = Enterprise Orchestration. The #1 iPaaS, with speed and power to orchestrate your organization’s data, apps, and processes, Workato is platform like no other. A secure, cloud-native runtime for any workload, any use case, any integration/automation pattern.
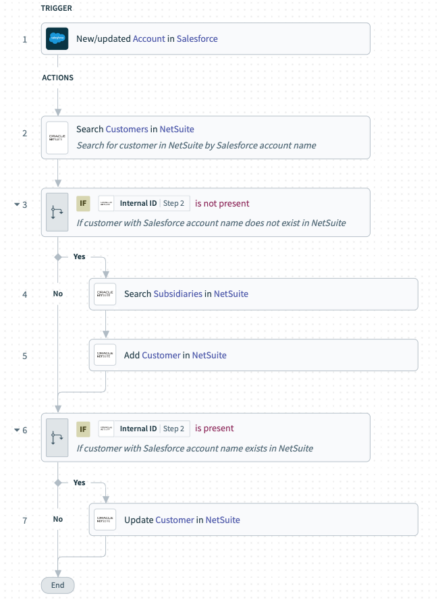
Workato helps you automate business workflows across cloud and on-premises apps. For example, automate quote-to-cash business processes which may involve transferring data between apps such as Salesforce, Netsuite, Bill.com, and Apttus.
Workato combines an enterprise-grade workflow automation platform with the ease of use expected from consumer apps, enabling both business and IT users to quickly build workflow automation.
Key Features of Workato:
- Embrace Versatility, Tame Complexity: Eliminate tool sprawl with one platform for all needs and unify your teams with a single experience. Focus on work that moves your business forward.
- Democratize Transformation: Accelerate success using our AI-powered no-code platform featuring over 1200 pre-built connectors and ready-to-use accelerators. Empower your teams to transform work.
- Scale Your Success with AI: Effortlessly integrate AI into your business processes, boosting efficiency and innovation for your business without sacrificing data privacy and control.
- Extensive Connector Library: Workato’s platform provides pre-built connectors to a wide range of applications, from CRM and ERP to marketing and support systems, allowing teams to easily integrate tools across departments.
- Low-Code/No-Code Capabilities: Workato’s user-friendly interface helps business users build and modify workflows autonomously, freeing up IT resources and accelerating innovation.
- Advanced Automation: Beyond basic integrations, Workato supports end-to-end process automation with capabilities like conditional logic and multi-step workflows. It also supports parallel tasks, enabling complex, dynamic workflows.
- Enterprise-Grade Security: Workato offers robust security and compliance features, including role-based access control and data encryption. It also provides audit logs, ensuring sensitive data remains protected across all integrations.
Conclusion
Effective integration solutions are crucial for organizations seeking to enhance operational efficiency, foster collaboration, and accelerate innovation. Understanding the different types of integration tools—such as enterprise service buses (ESBs) and iPaaS options like Workato—helps businesses choose the right solution.
This enables them to select tools that align with their specific needs.
Implementing a robust integration solution streamlines workflows, boosts scalability, and strengthens security. Choosing the right platform helps organizations eliminate data silos, promote cross-departmental collaboration, and reduce costs of manual integration.
With a comprehensive solution like Workato, businesses can maximize their data and applications, driving informed decision-making and sustainable growth.

Access all of these features with Workato
Workato, the leader in enterprise automation, enables your organization to integrate and automate at scale by providing more than a thousand pre-built connectors, a low-code/no-code UX, and much more.
