Application integration, or enterprise application integration (EAI), is the process of enabling cloud or on-prem applications to communicate with one another, typically via their application programming interfaces (APIs). This process is essential for a seamless data flow into a unified system for data transfer and synchronization. Without application integration, you would do more manual data entry.
Besides being able to automate and streamline data flow across applications, application integration is important for the following reasons:
- bridges the gap between on-premises and cloud applications and systems
- integrates legacy systems with modern applications, thus enabling more agile business operations
- supports automation, thus minimizing errors
- enables personalized and timely customer service due to your access to data in your integrated applications
We’ll review common ways to integrate your applications, the benefits application integration can bring to your organization, the tools you can use, and a whole lot more.
Related: Everything you need to know about enterprise application integration
Application Integration Use Cases
To give you a better sense of how application integration can work, let’s walk through a couple of use cases.

1. Notify Reps When Prospects Are Ready to be Contacted
As your marketers execute drip campaigns that build interest among prospects, your sales reps will want to know the moment when a prospect qualifies for a sales conversation.
You can do just that by connecting the customer relationship management (CRM) tool your sales reps work on and the marketing automation tool your marketers leverage.
For example, once the apps are integrated and lead data is synced between the two, a sales rep can learn when a prospect’s lead score reaches a level at which they’re sales-ready. That rep can then contact the prospect quickly and, in doing so, be more successful in their outreach.
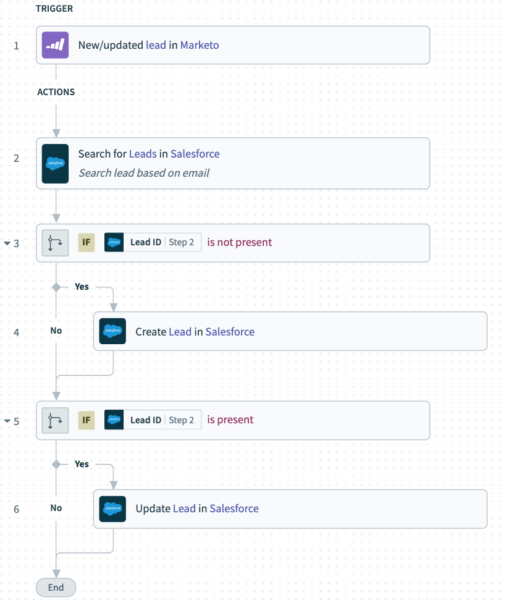
Related: Common application integration examples
2. Create Profiles for New Hires in Your HRIS Seamlessly
Once a candidate signs their offer letter, your organization will want to move quickly in setting them up with the appropriate tools and equipment. This ensures the new hire can hit the ground running on their first day. Plus, it can leave them with a positive first impression of your organization.
To help facilitate a high-performing onboarding experience, you can integrate a human resources information system (HRIS) and a recruiting tool. Then, build a data flow where once a candidate is marked as hired in the recruiting tool, their profile gets created in the HRIS.
Obviously, there are several more steps that need to be taken once the new hire’s profile gets created in your HRIS. An end-to-end workflow automation can help tackle them. But this, in and of itself, saves your team time and moves you one step closer to onboarding the new hire successfully.
3. Manage Client Invoices More Easily
As your organization grows its client base, it can become more difficult to keep tabs on individual invoices.
You can help your colleagues in finance manage each invoice more easily over time by syncing your enterprise resource planning system (e.g., NetSuite) with your organization’s business communications platform (e.g. Slack).
Once that’s done, set up the following workflow:
- A client is late on a payment.
- The appropriate employees in finance get notified via a message in a specific channel within your business communications platform.
- These employees can then move quickly in taking whatever steps are necessary to collect the payment in full.
4. Store Customer Documents in Accessible and Secure Folders
As sales reps upload a variety of important documents from clients in your CRM—whether that’s a fully-executed contract, a signed NDA, a contract amendment, etc.—the documents might not be accessible to the teams that need them, such as legal. And even those with access to your CRM might find the process of locating specific documents in the platform to be tedious and frustrating.
To help solve for all of the above, you can integrate your CRM with a file storage platform (e.g., Box) and then implement the following:
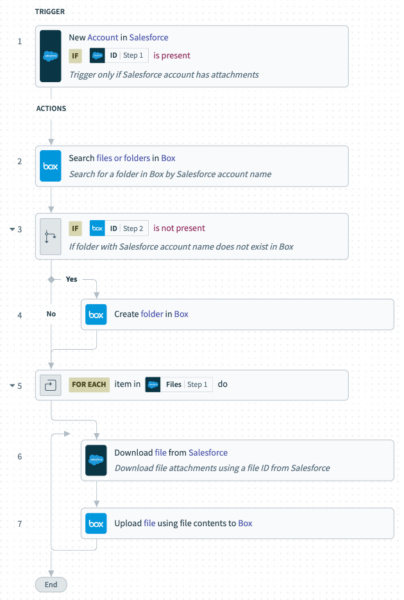
1. Once an account is added to Salesforce and it includes attachments, the workflow gets triggered.
2. If a folder associated with the account doesn’t exist, it gets added; if the folder already exists, the workflow moves on to the next step.
3. Each of the files from the account in Salesforce get downloaded and uploaded to a specific folder in Box.
5. Escalate Issues From an Outsourced Call Center Efficiently
Let’s assume that your organization uses a third party to manage clients’ issues. And while this third party can handle the majority of them, there are always exceptions that your organization needs to address. Whenever an issue falls in the latter, you’ll need to ensure that the right teams at your organization are made aware on time so that they can address the issue quickly.
To help solve this, you can connect the IT service management (ITSM) tools each party uses and then implement the following automation:

1. Once a support agent at the contact center escalates an issue within their ITSM tool (e.g., ServiceNow), the workflow gets triggered.
2. The escalated issue gets populated in your company’s ITSM tool (e.g., Zendesk), allowing the appropriate stakeholders to become aware of it.
3. Every time an employee at your company updates the issue, its changes get reflected in the corresponding ticket within the contact center’s ITSM tool, ensuring the contact center is kept in the loop.
Related: Common B2B integration examples
Benefits of Application Integration
There are a number of reasons why application integration is valuable for your organization. Here are just a few that are worth highlighting.
Fosters Healthy Collaboration Across Lines of Business
By providing accurate, matching data across your applications, lines of business can collaborate more effectively and deliver better bottom-line results for the business.
In more concrete terms:
- Sales reps and marketers can access the same information on prospects, allowing them to work in tandem throughout the prospect’s life cycle.
- Customer success managers (CSMs) and engineers can view escalated tickets and check on the status of any. This prevents each party from constantly asking the other for information, and it allows CSMs to provide accurate status updates to clients.
- CSMs and employees in accounts receivable can access the same invoicing data, enabling the latter to avoid reminding CSMs when one of their accounts is late on paying an invoice or hasn’t paid it in full.
Related: The benefits of enterprise application integration
Prevents Costly Errors
The process of manually reentering data across apps can quickly lead to human errors that negatively impact clients, prospects, employees, and job candidates.
Here are just a few examples:
- An employee in finance puts the incorrect contract value in the ERP system, leading to an invoice that charges the customer by the wrong amount.
- An employee in customer success copies a customer issue from the CRM platform to the ITSM tool, but accidentally inputs the wrong client.
- An employee in HR creates an offer letter that includes a lower salary and a different job title than what’s in the candidate’s profile in the recruiting app.
With application integration, employees by and large don’t have to worry about making these mistakes, as the data they put into one app can instantly carry over to others with complete accuracy.
Boosts Employee Productivity
Integrating your apps removes the need to constantly switch between them, as employees can access the data they need within the platforms they use every day.
This not only goes a long way in helping employees get meaningful time back, but it also allows them to focus more on thoughtful, strategic work that can deliver value to the business.
Lifts the Employee Experience
It’s little surprise that allowing employees to focus on more thought-provoking work isn’t just good for the business, but also for your employees’ satisfaction.
The vast majority of employees would go so far as to give up some of their salary just to feel like they’re doing important work. Meanwhile, nearly half of employees who are actively looking to switch jobs believe that their employer isn’t making full use of their skills and expertise.
In short, helping employees focus more of their time on thought-provoking work can help you retain them and keep them engaged.

Lets You Hold onto Valuable Legacy Systems and Adopt New Technologies
Certain legacy on-prem applications offer unique value that newer, cloud-based apps simply can’t address. Moreover, replacing one of these legacy systems can be an expensive, time-consuming proposition.
With application integration, you can hold on to these legacy systems, as well as use their data in new ways via the apps they’ve integrated with.
Related: How to integrate legacy systems with the rest of your tech stack
Cuts Down Costs
Application integration offers you the option of keeping your legacy system. Since you don’t need to eliminate your legacy systems entirely, you can save money and resources using new tools and services.
Another cost-saving effect of application integration is that it eliminates redundant processes and minimizes data silos. Thus, it allows you to save on resources and labor while improving overall efficiency.
Automate Workflows
Application integration allows you to automate workflows and focus more on manual tasks, simplifying and streamlining large-scale tasks. Automation enhances accuracy, freeing up employees to focus on higher-value tasks.
Related: Business benefits of enterprise application integration
Challenges of Application Integration
Application integration benefits your organization; however, the process isn’t straightforward. Here are some challenges of application integration.
Complexity of Legacy Systems
Most companies, especially old companies, use legacy systems for their processes. Sometimes, modern systems don’t support the data format of the legacy system. Legacy systems may also be less flexible and lack interoperability compared to modern alternatives.
Security Concerns
Security is a serious concern when discussing integration, primarily because it exposes sensitive data to new vulnerabilities. Thus, it’s important to implement robust security measures and use tools that comply with regulatory standards.
Data Inconsistency and Synchronization
The external application has data outside your enterprise’s core hold data. It also has different data formats and update cycles, often leading to data inconsistency, duplicate entries, errors, and duplicate records. You can, however, mitigate this issue with a robust data synchronization strategy.
Lack of Compatibility
Since you’re integrating with applications outside your ecosystem, your system might be incompatible with the vendor. This lack of compatibility issues will result in data silos, inability to automate tasks, operations, and inefficiencies. However, for situations like these, custom solutions come in handy.
Popular Types of Application Integration
Generally speaking, you can either build integrations in-house via custom code (otherwise known as point-to-point integrations), or use a third-party tool, which often takes the form of an integration platform as a service (iPaaS) or a legacy, on-prem middleware platform like an enterprise service bus (ESB).
Despite their inherent differences, both approaches share many of the same pros and cons.
Pros
- Data silos are eliminated, allowing employees to avoid app-hopping, data entry, and potential misalignment with colleagues.
- Employee satisfaction is likely to improve, as enabling employees to focus less on tedious tasks and more on strategic, meaningful work is proven to improve the employee experience.
- Employees are less likely to make costly errors, as they no longer need to perform as many manual, error-prone tasks.
Cons
- Implementing application integration can take precious time away from your dev team when they might have other critical tasks on their plates.
- As integration requests increase, your team’s integration backlog can quickly balloon.
- Your organization is left vulnerable when the developers who understand specific integrations leave your company, as remaining employees may not know how to fix or improve the integrations.
- The timeline for building the integrations can be long, which causes data silos to persist and business partners to be unhappy.
How to Evaluate Application Integration Solutions
Despite many platforms having a common set of pros and cons, they often differ in notable ways. To help you find the one that’s best for your business, you can use the following criteria when reviewing them.
Ease of Use and Governance
A low-code/no-code application integration tool can enable employees across lines of business to build impactful integrations and give IT and engineering some time back.
That said, to ensure that your data, business applications, and processes remain secure as additional builders participate, you’ll also need the platform to offer enterprise-grade security. Look for features like activity audit logs and role-based access control (RBAC) to ensure this.

AI and Machine Learning
The platform should leverage the latest in AI and machine learning to help builders implement intelligent, high-performing integrations.
For example, if you’re looking to integrate an application like Salesforce with an ITSM tool like Zendesk in order to keep accounts in sync, the platform can intelligently suggest the fields that can be mapped between them.
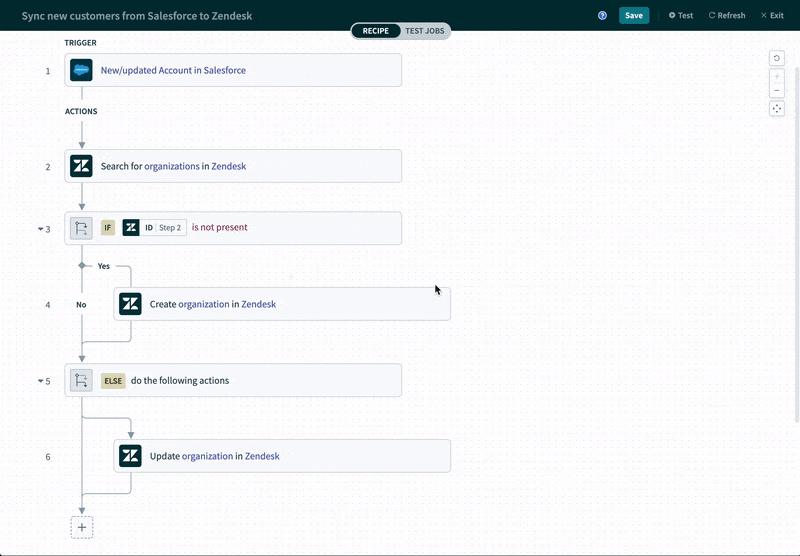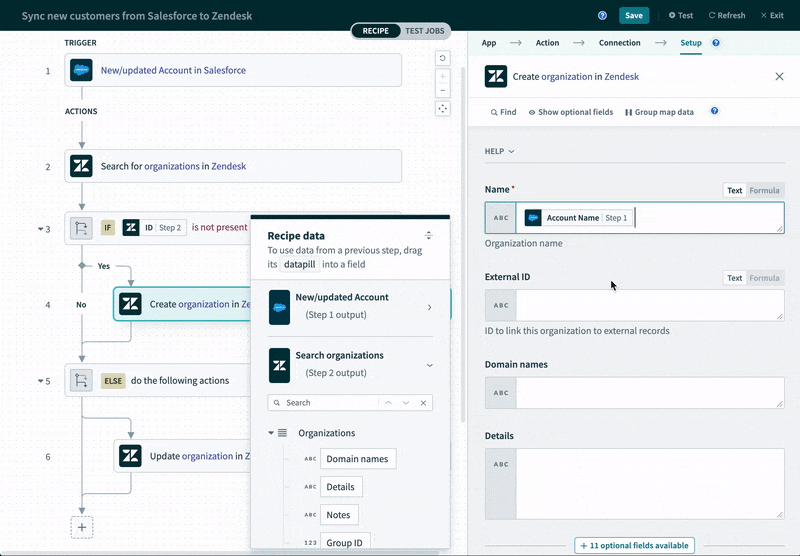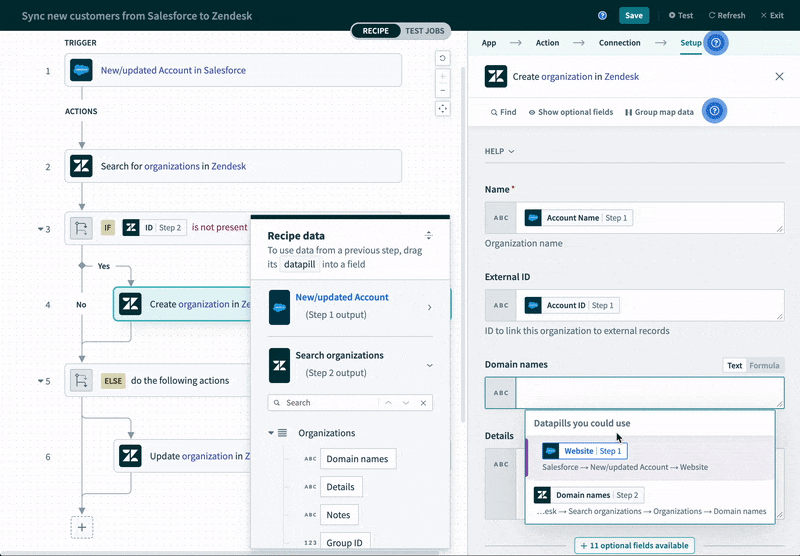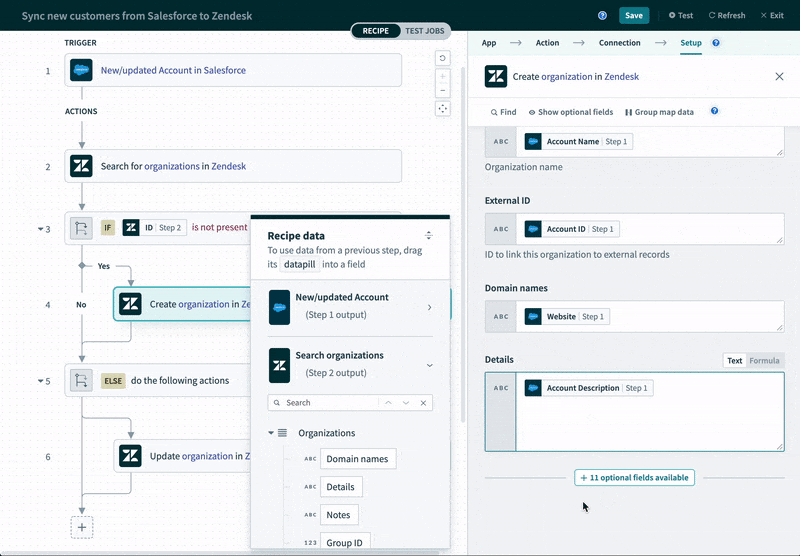
Workflow Automations
While application integration is useful in and of itself, your path to digital transformation shouldn’t stop there.
One of the key use cases application integration enables (and that the platform you select should offer) is end-to-end workflow automations for critical business processes.
Specific business events can trigger these workflow automations in real time. Your team can then use this workflow automation for a number of business processes, whether it’s lead routing, quote-to-cash, incident management, etc.
Enterprise Platform Bots for Business Communications Platforms
Your employees likely spend a significant chunk of their time working from a business communications platform like Slack or Microsoft Teams.
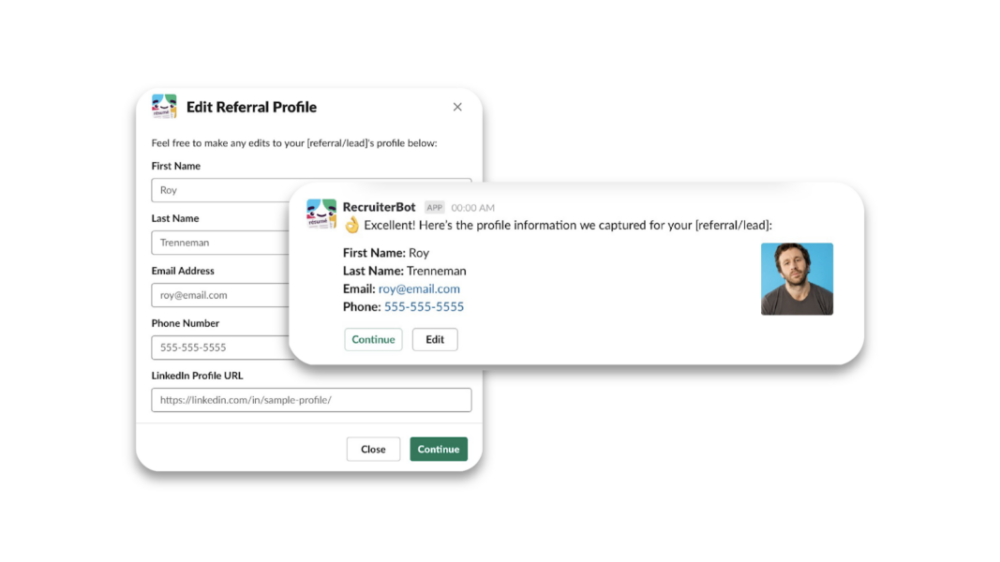
With that in mind, you should look for a solution that offers platform bots that can bring data from third-party applications and automation directly to employees in your business comms platform.
Say you’ve built an automation around referring candidates. To kickstart the automation, an employee can access the platform bot you’ve built within your business comms platform and fill out a form that includes all of the required information.
Pre-built Connectors and Automation Templates
While many integration solutions provide pre-built connectors for SaaS applications, databases, or on-prem systems, their connectors will vary by breadth (i.e., the connectors they’ve made available) and depth (i.e., each connector’s scope of functionality).
With this in mind, you’ll need to do some research on the connectors each platform provides, their plans for enhancing them, and their roadmap for launching new ones.
Similarly, many platforms offer a library of automation templates to help you brainstorm and implement automations more easily. Take some time to review the ones each vendor has made available. If possible, try to also find out about the templates they plan to release over the coming months.
Coming up With an Application Integration Strategy
Given that every organization has a unique set of applications, data, processes, and business goals, they’ll need to arrive at their own application integration strategies.
That said, addressing the following questions in sequential order can help you land on the strategy that’s best for your business.

1. What Are Your Business Goals From Implementing Application Integrations?
This can be anything from saving time and becoming more efficient to enabling end-to-end automations that can transform your business processes.
2. What Are the Scenarios and Use Cases That You’re Looking to Support?
In other words, what types of systems, processes, and data are you looking to integrate?
3. What Are the Nonfunctional Requirements for Your Application Integrations?
You can think about this through a number of dimensions, such as reliability, scalability, and compliance.
4. What Delivery Model Are You Looking to Adopt?
The answer largely depends on the goals you set earlier.
For instance, if you’re looking to save time, it might make sense to use a centralized model where IT manages the integrations end-to-end.
On the other hand, if you’re hoping to innovate, you should look to adopt a decentralized delivery model where business teams can help build and manage the integrations (while IT oversees their activities and the integration platform that’s used).
5. What Technology Platforms Should You Invest in?
Based on your functional and nonfunctional requirements, as well as your desired delivery model, you should be able to pinpoint the application integration solutions that fit your needs best.
Finally, it’s worth going through this exercise on a recurring basis (e.g., once a year) so that your strategy can adapt to changes in the market, your technology stack, your business goals, etc.
Wrapping up
Application integration is particularly important because every organization relies on multiple tech stacks. Thus, you can describe it as the missing piece for unifying your technology landscape. This is because it allows you to integrate with diverse applications, work seamlessly with them, and share data in real time.
Since application integration can give you a competitive edge, you should prioritize efficiency and agility by going for a tool like Workato, the leader in enterprise automation. Workato offers a low-code/no-code UX; hundreds of thousands of automation templates; Workbot, a customizable platform bot for Slack and Teams; and much more. Schedule a demo today.

Get your integration & automation needs met with Workato
Workato, the leader in enterprise automation, offers a low-code/no-code UX, hundreds of thousands of automation templates, Workbot, a customizable platform bot for Slack and Teams, and much more.
FAQs
What Are Some Important Concepts Within Application Integration?
While it’s hard to list all of them, here are some important concepts that you should understand before you start integrating your applications:
- Application programming interface (API): Depending on who you ask, it’s either all of the endpoints or an individual endpoint that an organization has made available for accessing specific data or functionality.
- Data mapping: It’s the process of mapping the data model of one application with the data model of another.
- Webhooks (or “reverse API”): It’s an integration technique that allows you to handle events or event-based actions in near real time.
What Is Data Integration?
Data integration is the process of extracting data from a multitude of sources, transforming that data to a common data model, cleansing it, and then uploading it to a single place, such as your data warehouse.
You can then use the data for analytics with business intelligence (BI) and analytics tools, allowing your analysts to uncover actionable business insights on time.
What Are the Differences Between Application Integration and Data Integration?
While the two approaches are merging over time, a key difference is that the downstream applications involved in each approach will likely differ. More specifically, data integration is mostly for analytics and BI tools, while application integration can apply to any other type of application.
What Is Software Integration?
Software integration is the process of connecting software applications with one another, often through their APIs.
What Is the Difference Between an API and Integration?
APIs are only one integration method. You can also perform integrations at the UI level, through files, or other means.