Data integration and application integration are often incorrectly treated as one and the same.
This can lead to miscommunication between teams, misusing either approach, and neglecting at least one of the approaches altogether.
To help you and your team get on the same page, we’ll break down how the two differ by walking through their definitions as well as examples of how they can work. We’ll then share how—despite their inherent differences—they’re beginning to overlap in interesting ways.

Integrate your applications and data with Workato
Learn how Workato, the leader in enterprise automation, lets you implement data and application integration without having to write a line of code.
What is data integration?
Simply put, data integration is the process of collecting data from several data sources, transforming it, and then loading it into a data warehouse (i.e. following an ETL process). From there, your analysts can retrieve the data and use it in the analytics and business intelligence (BI) tools they rely on.
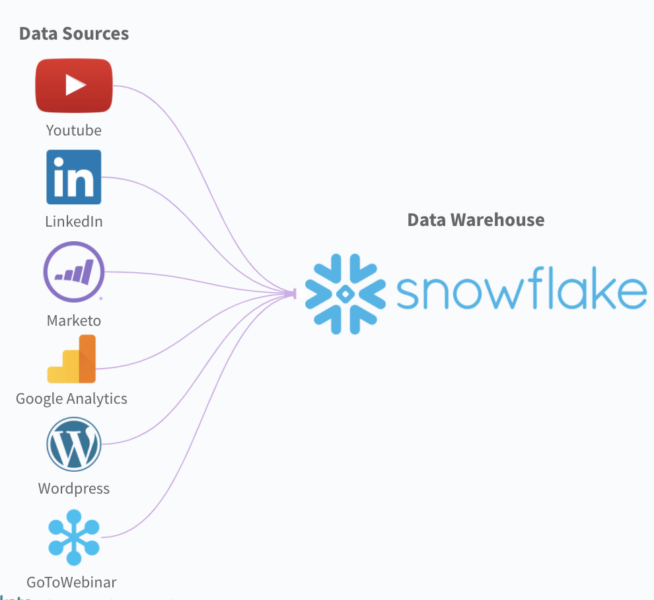
The clear benefit of data integration is that it allows your team to gather all the data that’s needed before beginning their analysis. This allows them to arrive at better decisions, both for their function and for the business more broadly.
A clear con, however, is that historically (and even to this day), organizations have approached data integration with a batch-oriented process. This means that data would move to the data warehouse on a consistent cadence but in a way that was far from real time (e.g. once per day)—preventing analysts from accessing and leveraging more recent data.
Related: A look at data integration’s benefits
What is application integration?
Application integration is the process of keeping your apps in sync when an event or data changes in one of them. This normally involves using their application programming interfaces (APIs) as a means for communicating with each other.
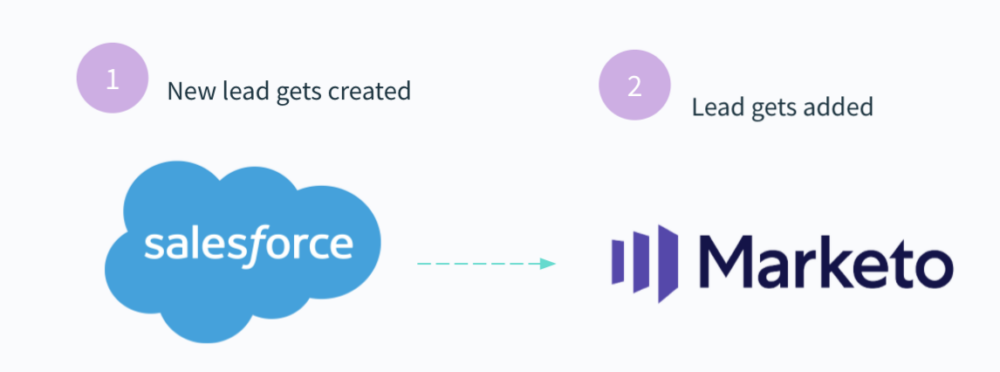
Application integration provides your team with various benefits:
- Your applications are kept up to date, allowing employees to access and use the latest information
- Human errors (caused by manual data entry) that could create significant issues down the line, such as sending a client an inaccurate invoice, are avoided
- Employees can save time, as they no longer have to move between apps and engage in extensive data entry
However, like data integration, application integration has often been done using a batch process, which prevents data from getting added in real time. For example, once a new lead gets created in your CRM, your marketing automation tool—among other tools affected—would only add the lead several hours later. As a result, your marketers might lose valuable time in nurturing the lead simply because they’re unaware it exists.
Related: Examples of application integration
How application integration and data integration are coming together
Today, the two are overlapping in various ways.
- Data can move at or near real time. Organizations are now expected to use this approach—over the batch method—for both data and application integration so that employees can access more accurate, up-to-date data in their apps.
- Application integration also involves retrieving data from a data warehouse. Since data integration already provides data to your warehouse, application integration can simply involve taking the data that’s in the warehouse and moving it to downstream tools in real time.
- Teams are coming together to tackle both approaches. Now that both methods involve moving data from the data warehouse to downstream apps, the business analytics team (responsible for managing data integrations) and the business technology team (responsible for managing application integrations) can work alongside one another to fulfill their respective goals.
Data integration vs application integration
Application integration and data integration function in increasingly similar ways; the only clear difference between them are the downstream apps that are typically involved with each and the teams who have access to those apps.

Integrate your applications and data with Workato
Learn how Workato, the leader in enterprise automation, lets you implement data and application integration without having to write a line of code.
Data integration and application integration FAQ
In case you’re not fully clear on either integration approach or on how they differ, we’ve answered several more questions below.
What are some popular application integration tools?
Some common application integration platforms include Workato, Mulesoft, Boomi, and Jitterbit. Workato stands out from others in this categority in that it allows you to do much more than integrate your apps. For instance, it lets you automate workflows end-to-end, build customizable platform bots for Slack or Teams, develop, publish, and maintain APIs, and more—all within a low-code/no-code UX.
What are some common data integration tools?
The list includes vendors like Workato, Fivetran, Talend, and Informatica. Workato, however, also allows you to perform additional integration and automation use cases through its low-code/no-code UX. This ensures that lines of business can also play a role in developing and maintaining integrations and automations and that your organization can address all of its digital transformation requirements.
When should you use data integration over application integration (and vice versa)?
The approach you choose should depend on the goals of your integration scenario. If you’re looking to sync data across specific applications, it might make more sense to use application integration; while if you’re looking to analyze and make decisions off of a broad set of information, it’d make more sense to perform data integration.