The Internet of Things (IoT) is reshaping how we connect and interact with technology. By linking everyday devices to the internet, IoT turns ordinary objects into smart tools that collect and share data. With billions of IoT devices projected in the coming years, the innovation potential is immense.
To fully leverage these advancements, integrating IoT into your existing systems is crucial. IoT integration connects devices with your applications and databases, enabling streamlined data flow and automation. In this guide, we’ll explore the importance of IoT integration and provide practical insights on how to implement it effectively, using real-world examples.
What is IoT?
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to devices that collect and exchange data over the Internet. These devices collect and exchange data over the Internet, turning everyday objects into intelligent tools. Currently, there are billions of IoT devices worldwide, and their numbers are rapidly increasing. Businesses and homes are adopting them for enhanced convenience and efficiency.
The Internet of Things (IoT) encompasses devices like smart thermostats, fitness trackers, and connected security cameras. For example, a smart thermostat adjusts the temperature when it detects that you’re home. Wearable fitness trackers monitor your activity and health metrics. Connected security cameras send alerts if they detect unusual movement. All these devices communicate over the internet, turning everyday objects into intelligent tools. As IoT devices proliferate, they become integral to modern life, shaping how we interact with technology.

What is IoT integration?
IoT integration connects smart devices, your applications, and your databases. Linking a smart thermostat to your home automation system allows temperature adjustments based on your schedule. Integrating wearable fitness trackers with health apps lets you monitor and analyze your activity data. This connectivity enables seamless data flow and automates processes, optimizing operations and providing actionable insights. With billions of IoT devices in use today, integration is key to leveraging their full potential and enhancing efficiency across various domains.
Related: The definition of business process integration
Key Questions in IoT Integration
1. What is an IP Address in IoT and How Is It Used?
An IP address uniquely identifies each IoT device on a network, enabling it to communicate with other devices and central systems. For example, it allows a smart thermostat to send temperature data to a home management system, ensuring precise control over your environment.
2. What Is the Purpose of an IoT Gateway and How Does It Function?
An IoT gateway connects IoT devices to the internet or other networks, handling data collection, processing, and forwarding. It acts as a bridge, translating and filtering data to ensure efficient and secure transmission to central systems. This function is essential for maintaining the integrity and usability of the data.
3. What Are the Functionalities of Data Integration Tools Like Embedded iPaaS in IoT?
Data integration tools, such as embedded iPaaS, play a crucial role in connecting IoT devices with various applications. iPaaS, or Integration Platform as a Service, is a cloud-based solution that simplifies these connections by providing a unified platform for integrating disparate systems and applications. It allows for seamless data exchange between IoT devices and your systems, automating workflows and ensuring efficient data flows.

Key functionalities of iPaaS include real-time data exchange, which ensures timely updates and interactions; data mapping, which aligns data formats between different systems; and API management, which facilitates communication between applications. These tools help streamline the integration process, making it easier to manage complex data interactions and enhance operational efficiency.
Examples of IoT integration
Let’s bring this definition to life by walking through some examples.
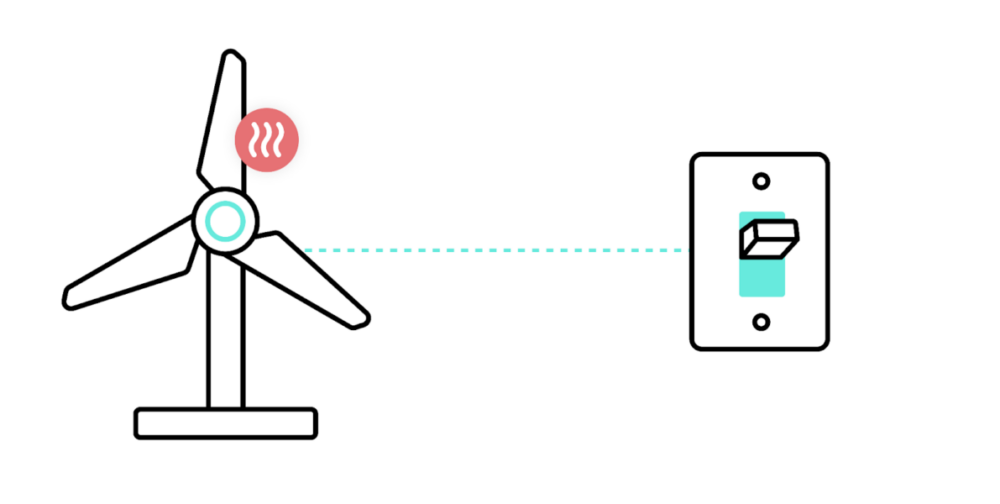
1. Prevent windmills from overheating
Left unattended, a windmill’s generator can overheat and, eventually, explode and cause fires.
To ensure this doesn’t happen, you can use sensors inside a windmill that monitor the generator and send temperature readings once per second to an IoT hub, or a computer that resides close to the windmills. The computer consolidates the data and then streams it to a consolidated data store (or a time-series database). That data is then added to an analytics or BI tool, where employees can run queries, uncover insights, and monitor the temperatures of the windmills’ generators.
Since relying on people to monitor and analyze the windmills’ temperatures at all hours is expensive, difficult, and unpleasant, you can lean on automation for support. For example, you can build an automation where if a generator were to reach a certain temperature, an IoT switch would temporarily turn it off.
Related: 3 chatbot automation examples
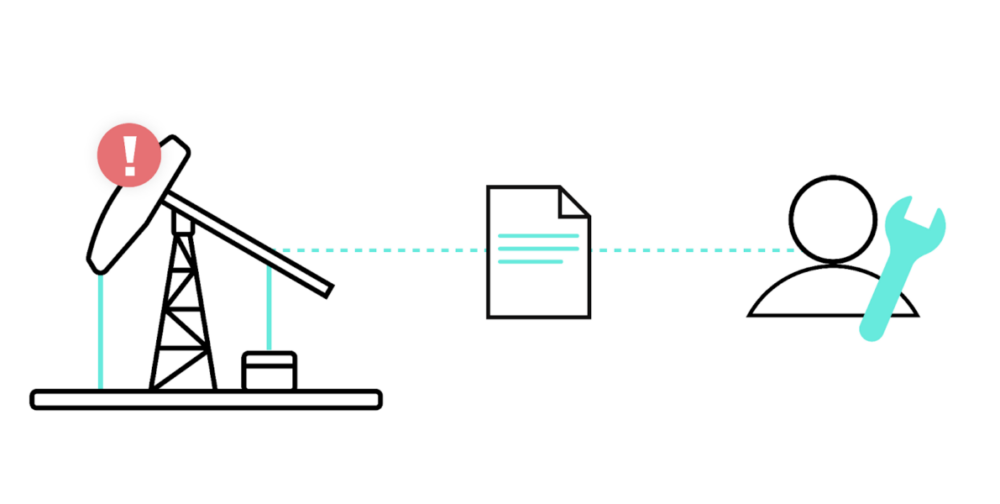
2. Replace oil pumps proactively
Oil companies should identify when certain pumps need to be replaced well before they’re unfit for use. Otherwise, these organizations could be dealing with unused oil wells for extended periods.
To help oil companies identify the ones that are reaching their expiration, they can put sensors in the pumps that monitor certain health signals, such as the speed at which a pump is rotating.
Once these signals reveal that a pump is near the end of its use, you can trigger an automation where a work order is automatically created for replacing it.
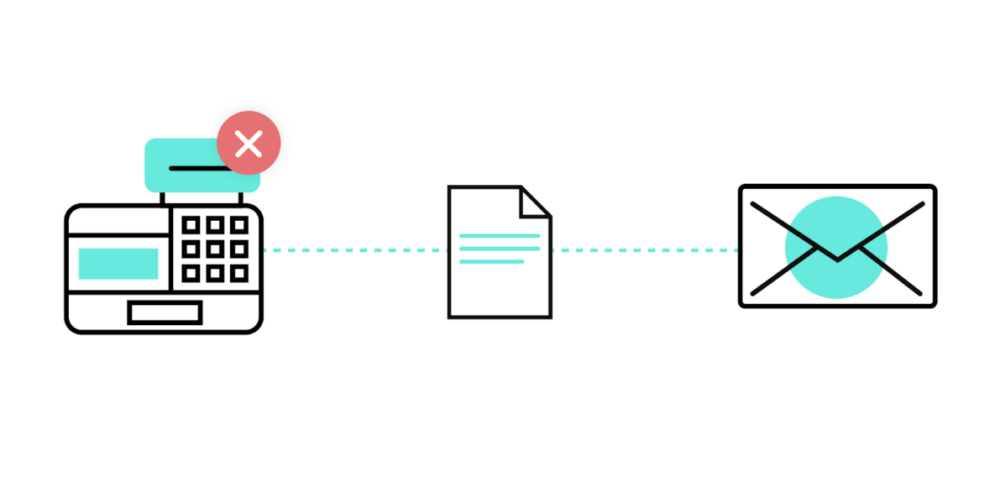
3. Identify failing POS devices
Similar to our previous example, organizations that manufacture and sell point-of-sale, or POS, devices (e.g. Toast) can use sensors to determine when a device needs to be replaced. Only in this case, they’d make the judgment based on the increasing number of times that a credit card needs to be swiped in order to process a sale.
Once the error rate reaches a certain threshold, you can trigger an automation that creates an order for a POS device and initiates other steps for shipping out the device to that business. In addition, along with the device, you can include a note that explains why your client is receiving a replacement.
Note: While the three examples above are powerful IoT integration use cases, an integration platform as a service (iPaaS) solution is better at handling the last two. The reason is, that an iPaaS solution isn’t well-suited to stream high volumes of data, but it can trigger and streamline workflows across your applications effectively.
Related: 5 application integration use cases
Benefits of IoT integration
Here are just some of the benefits of implementing IoT integration:
Lower costs
By using sensors to monitor equipment, you can manage the equipment in ways that maximize uptime and prevent under-performance.
For instance, in our oil pump example, IoT integration can save you from not being able to pump oil from an oil well for several days; instead, you’re able to replace pumps proactively, which might take just a few hours. This difference, when applied across all the wells your organization uses, can amount to millions of dollars in cost savings per year.
Related: The top benefits of intelligent automation
Reduce risks
IoT integration can help your team identify potential risks in real time and move swiftly in minimizing them.
Our windmill use case exemplifies the risk that exists without IoT integration: overheated generators can cause fires that not only lead the windmills and the surrounding equipment to burn down but can also harm your employees.
Delight clients
Using IoT integration, your team can deliver unexpected experiences that satisfy clients and ensure they keep using your equipment effectively.
Our use case around replacing POS devices proves this point: giving clients a new POS device before they even need it shows how committed you are to supporting their business and ensuring they get full use out of your product.
Enable employees
Forcing your team to constantly monitor data and decide on the actions they take from it can be extremely time-intensive. Moreover, your employees are forced to spend less time on the business-critical, strategic work they likely enjoy more and are better suited to perform.
IoT integration can take some of the load off your employees, as it lets you build trigger-based automations that work off of sensor data and that only call for human intervention when necessary (e.g., mailing out a POS device to a client).
Enhance environmental sustainability
IoT integration optimizes resource use, reduces waste, and improves overall sustainability. By monitoring and managing energy and resource consumption more effectively, organizations contribute to a greener environment.
Ready to Implement IoT Integration?
Define Your Goals: Start by pinpointing what you want to achieve with IoT integration. Identify specific issues or processes you want to improve, like equipment maintenance or customer engagement.
Choose the Right Devices: Select IoT devices that match your needs. For example, if monitoring machinery, pick sensors that provide real-time, accurate data.
Pick an Integration Platform: Use an integration platform to connect IoT devices with your systems. Platforms like Workato provide pre-built connectors and automation tools to streamline data flow.
Set Up IoT Gateways: Deploy IoT gateways to manage data transfer between devices and central systems. Gateways ensure data is collected, processed, and sent efficiently.
Create and Test Workflows: Develop workflows that automate actions based on IoT data. For example, set up alerts for maintenance when sensors detect issues. Test these workflows thoroughly before full deployment.
Ensure Security: Protect your data with strong encryption and secure authentication methods. Make sure your IoT setup complies with relevant regulations to keep your data safe.
Monitor and Improve: After implementing, keep an eye on system performance. Use analytics to fine-tune processes and ensure your IoT integration meets your objectives.
Ready to simplify your IoT integration?Explore how Workato can help.
Conclusion
As connected IoT devices become more prevalent, effectively integrating them can transform your business operations. IoT integration allows you to leverage real-time data from devices, driving efficiency, reducing costs, and enhancing decision-making. By connecting IoT devices with your applications and databases, you enable automation, improve risk management, and offer exceptional customer experiences. To implement IoT integration effectively, consider using platforms like Workato, which streamline the process, support real-time data exchange, and ensure seamless connectivity across your systems.
Embrace IoT integration to stay competitive and make the most of your technological investments.

Ready to implement IoT integrations?
Workato, the leader in enterprise automation, lets you implement end-to-end automations that work across your IoT devices, applications, and databases.