Intelligent automation is no longer what many claim it is.
Its previous form—where it involved using robotic process automation (RPA) software, a business process management (BPM) tool, and AI capabilities (e.g. intelligent document processing)—was riddled with issues.
RPA has proven to be brittle and unscalable; its bots can break with any small UI change and the process of building and managing more bots requires adding personnel with technical expertise. Add to this BPM’s inherently limited functionality, and it becomes clear that intelligent automation is not the transformative solution that organizations once imagined.

Performing intelligent automation today requires your organization to integrate all of their applications for a given process at the API-level, including AI and ML-based tools. Your organization should then build workflow automations that work across these connected systems.
We’ll show you how intelligent automation can work in practice, but first, let’s take a step back and formally define the term.

Ready to implement intelligent automations?
Learn how Workato, the leader in enterprise automation, can help you leverage AI and ML when building end-to-end automations.
What is intelligent automation?
It’s an automation that uses AI or machine learning to optimize or transform a business process. This requires using two separate tools that can interact with one another: one is capable of building and managing automation, and the other(s) is an AI or ML-based tool.
How different is intelligent automation from automation?
You might wonder what the differences are between automation and intelligent automation. Let’s take a look.
| Features | Automation | Intelligent automation |
| What does it do? | Uses technology for performing repetitive tasks. | Combines automation with machine learning and artificial intelligence to make decisions. |
| Complexity | Works to perform simple repetitive tasks. | Works with dynamic and complex operations. |
| Adaptability | Follows certain predefined workflows and rules. | Learns, adapts with scenarios, and improves over time. |
| Decision making | Can’t make any decisions. | Uses AI for analyzing data and making decisions. |
| Example | Rule-based automationScript-based data entry | Predictive analytics.AI-powered chatbots. |
We will discuss some more examples of intelligent automation in the coming sections. But before that, we will learn about the key components of intelligent automation.
Key components of intelligent automation
As discussed, intelligent automation integrates advanced technologies to make the systems adaptive and smarter by enhancing automation. The key components are –
Robotic process automation (RPA)
RPA enhances efficiency by automating rule-based tasks.
Process mining and analytics
Optimizes workflows by identifying inefficiencies.
AI and ML
AI enables systems to recognize patterns by analyzing data and make decisions. ML, on the other hand, helps to improve automation over time by learning from user interactions and data.
Natural language processing (NLP)
This allows machines to understand human language and respond accordingly.
Intelligent decisioning
IA uses insights driven by AI to enhance decision-making and automate complex tasks.
Now that we have learned about the components, let’s take a look at a few detailed examples of intelligent automation.
Examples of intelligent automation
Here are just a few examples of intelligent automation.
Leverage machine learning to classify support tickets
A machine learning model is only as powerful as the quality and quantity of data it receives.
You can ensure that your ML solution receives a high volume of valuable data by using an enterprise automation platform to integrate it with a variety of source systems. Once connected, the enterprise automation platform can pull data from a variety of sources, cleanse it, validate it, and then load it to your ML solution. Once it receives enough data, the machine learning model can draw predictions or make a decision, which can trigger the appropriate workflow automation.
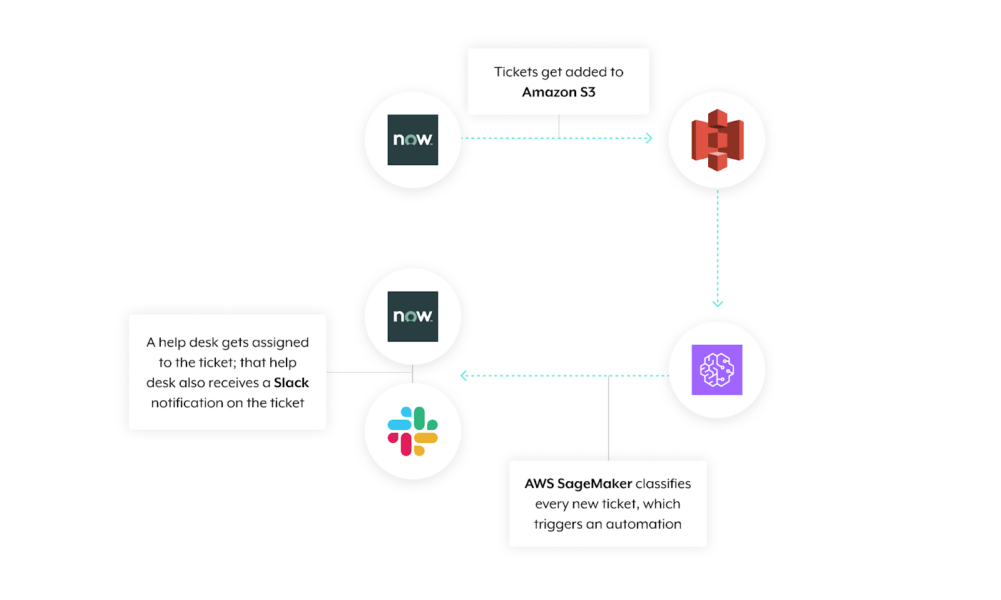
For instance, say your organization has thousands of employees across the globe. As a result, your IT team receives a high volume of support tickets, 24/7; this makes the prospect of classifying and routing tickets to the appropriate IT help desk quickly near impossible.
To help streamline this routing process, you can connect your ITSM tool (e.g. ServiceNow) with a storage solution like Amazon S3. You can then send countless tickets to the latter so that Amazon SageMaker can deploy an ML model that accurately classifies each ticket.Once a ticket is classified by Amazon SageMaker, an automation gets triggered: the ticket gets assigned to the appropriate IT help desk, and to ensure that the personnel within that help desk are made aware of the ticket quickly, they receive a message in a channel within your business communications platform (e.g. Slack).
Provide an intelligent helpdesk
Your employees will likely have the same set of questions over time—whether that’s related to insights on a competitor or your company’s holiday schedule.
Instead of having employees ask one another for the answer or forcing them to search in your knowledge base, you can provide them with what they’re looking for in a matter of clicks within your business communications platform.
At the foundational level, you can use an enterprise automation platform to connect a solution that uses natural language processing (NLP), like IBM Watson, with your knowledge base software platform (e.g. Confluence). You can then implement the following automation:
1. An employee accesses a customized chatbot (e.g. “Knowledge Bot”) in Slack that’s powered by an enterprise automation platform.
2. The employee asks the bot a specific question, such as “How do I set up 2FA?”
3. Using NLP (via IBM Watson), the chatbot is able to understand the question’s intent. It then searches for the relevant article(s) in Confluence and, in real-time, returns at least one option.
4. If the employee finds the article helpful, they can click “Yes”, leading the chatbot to then show the entire article in a message. If they click “No”, the employee can reenter their question. And if that still doesn’t help, they can click “File a ticket”.
Related: How to automate your service desk
Benefits of intelligent automation
Here are just a few reasons to invest in intelligent automation:
Saves employees time
Employees who lean on artificial intelligence and machine learning for decision-making can save a significant amount of time. This is especially true when the scale of making a certain type of decision increases. For instance, as the number of tickets filed by your teams grows, using ML to classify them amounts to greater time savings.
Minimizes human errors
Performing tedious, repetitive tasks can leave your employees prone to making costly mistakes. Perhaps an employee mistakes the sentiment in a ticket and therefore misclassifies it—leading the issue to persist longer; or maybe someone in HR sends their colleagues an outdated holiday calendar by accident, motivating the employees to work or take time off when they shouldn’t.
Intelligent automation can help prevent these situations, and many like them, from taking place, as automation can remove or limit human intervention.
Delivers a better employee experience
Intelligent automations enable employees to focus less on mundane, time-intensive tasks, which ultimately frees them up to tackle the more challenging, thoughtful projects they crave.
In addition, intelligent automations can allow employees to stay in your business communications platform when performing tasks or searching for information, which should not only save them time but also help them avoid the unpleasant activity of moving from app to app to find what they need.
Related: The top benefits of office automation
Improves the customer experience
Similar to how automations that use NLP, or natural language understanding (NLU), can help IT manage internal tickets, they can also be applied to managing customer relationships, whether that’s through tickets, chat messages, or emails.
In other words, intelligent automation can answer questions on customer support reps’ behalf or classify each issue and then assign it with the appropriate level of urgency before routing it to a support rep. This likely translates to a faster time to resolution, which should go a long way in delighting clients and in helping them see more value from your platform.
Influences bottom-line improvements
Keeping employees engaged and satisfying customers isn’t optional—it’s business critical. According to a Forbes article, a whopping 88% believe that proper customer service is highly or extremely important to their organization’s success. In addition, based on Gallup’s research, business units in the top quartile of employee engagement are 23% more profitable than those in the bottom quartile.
Although immensely beneficial, intelligent automation comes with certain challenges. We will discuss those in the next section.

Challenges and limitations of intelligent automation
Some of the notable challenges of intelligent automation are –
Complexity
Seamless coordination with existing workflows and systems can make integration a bit complex.
Cost
Companies need to make a significant investment in RPA, AI, and infrastructure.
Data quality issue
Poor data quality can lead to inaccuracy of the AI model and inefficient decision-making.
Limitations of human-like understanding
AI faces problems while dealing with unstructured data, nuanced decision making, and contextual awareness, especially while facing ambiguous situations.
Maintenance
Continuous system updates, monitoring, and regular optimization are needed to maintain efficiency. This increases the maintenance cost.
Workforce resistance
Employees may get the fear of losing their jobs, leading to reluctance in upskilling programs and adoption.
Security
Since sensitive data needs to be handled, data privacy and compliance with regulatory standards are a big concern.
The future of intelligent automation
The relationship between an enterprise automation platform (or any integration/automation tool) and AI and ML tools should stay consistent over time. More specifically, enterprise automation platforms will continue connecting to AI/ML tools to unlock their capabilities as part of workflow automations.
That said, AI and machine learning tools will undoubtedly evolve and improve, and new solutions will continuously be released. As these innovations unfold, intelligent automation’s use cases and potential impact on organizations should only grow.

Implement intelligent automations with Workbot®
Workbot, Workato’s customizable chatbots for Slack, Microsoft Teams, or Workplace from Meta, can power intelligent automations while keeping your employees from leaving your business communications platform.