Summary
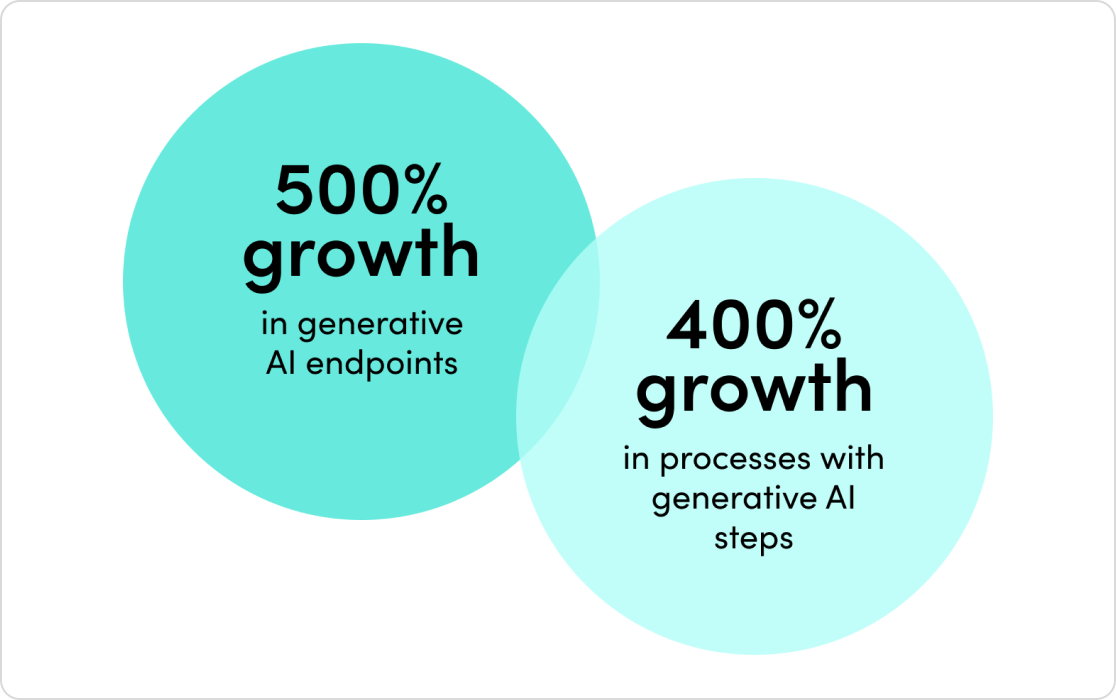
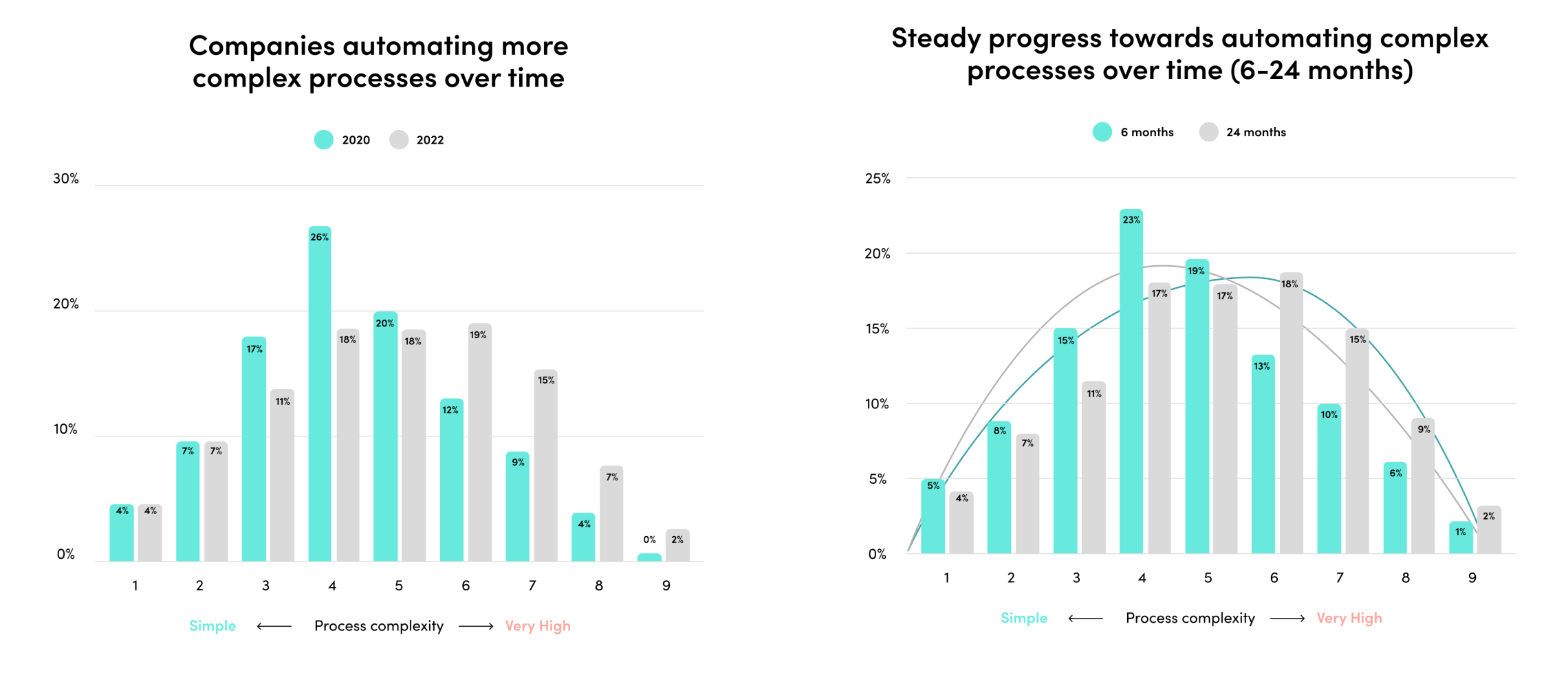
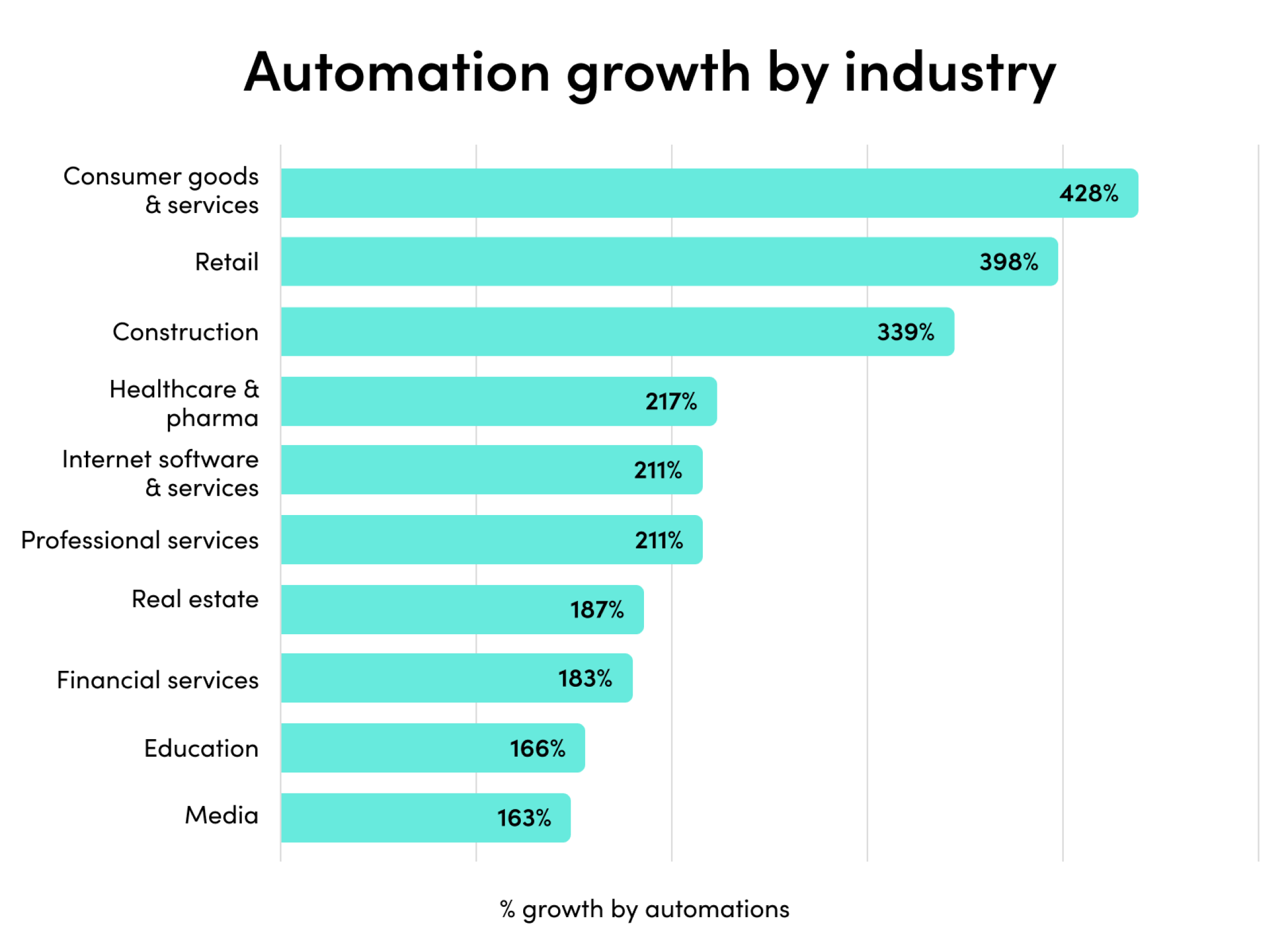
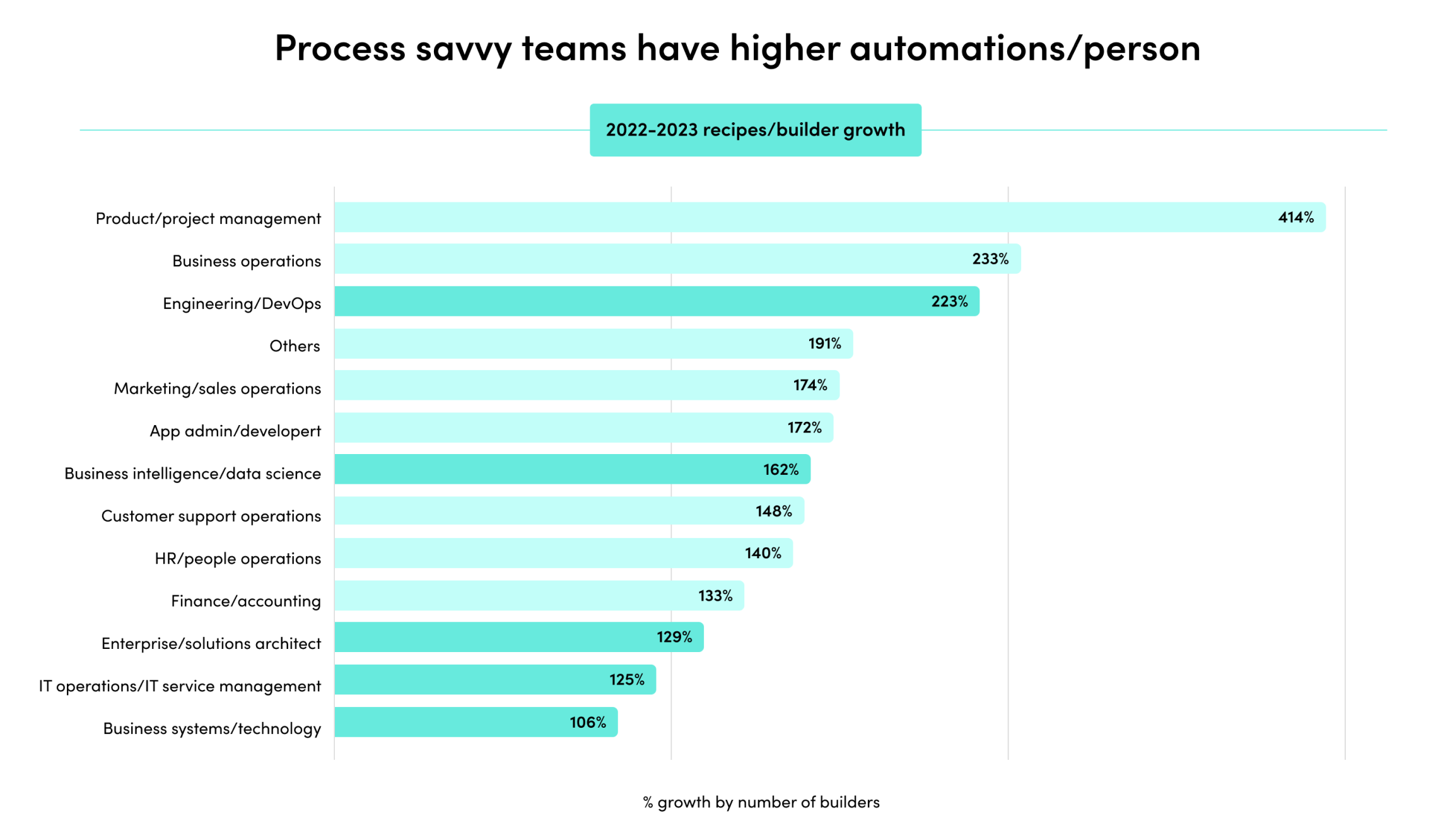
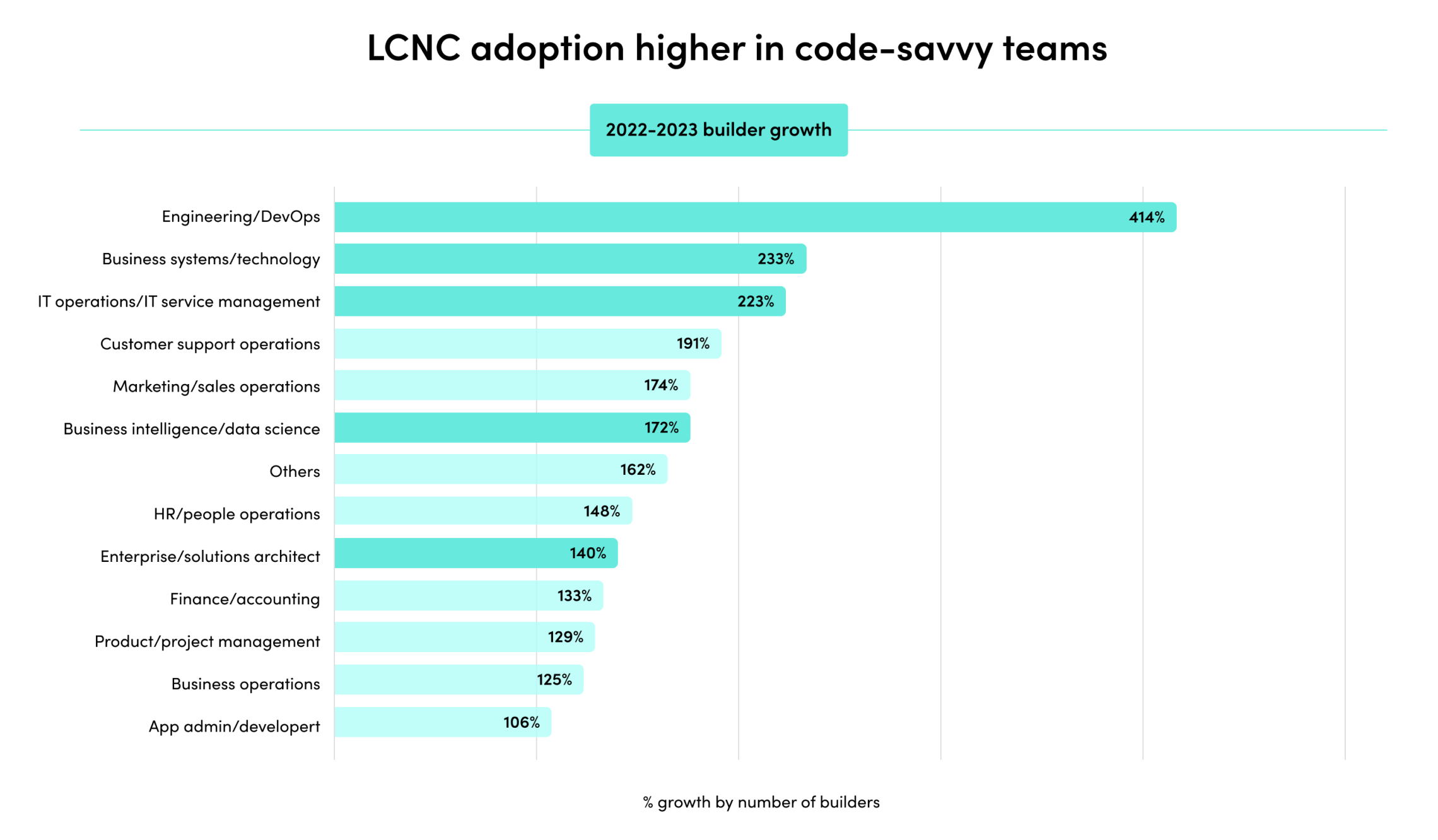
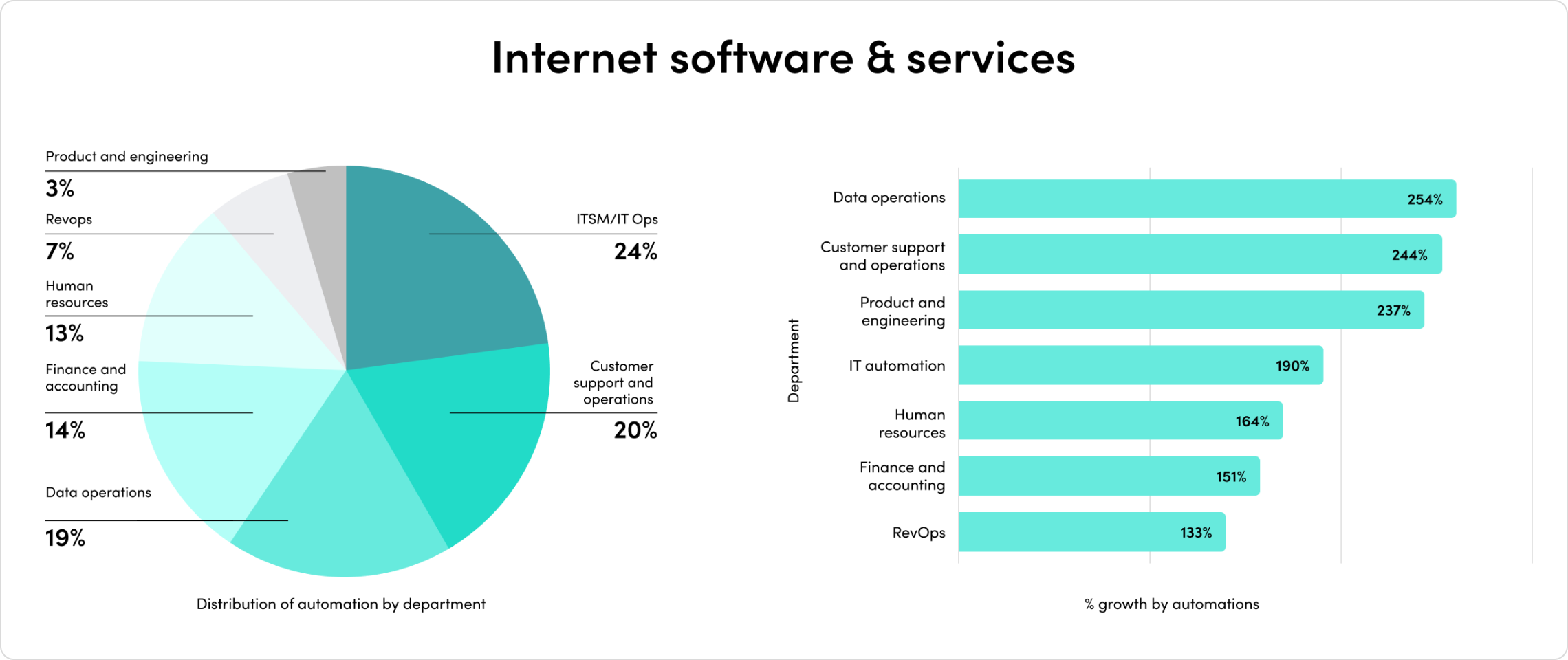
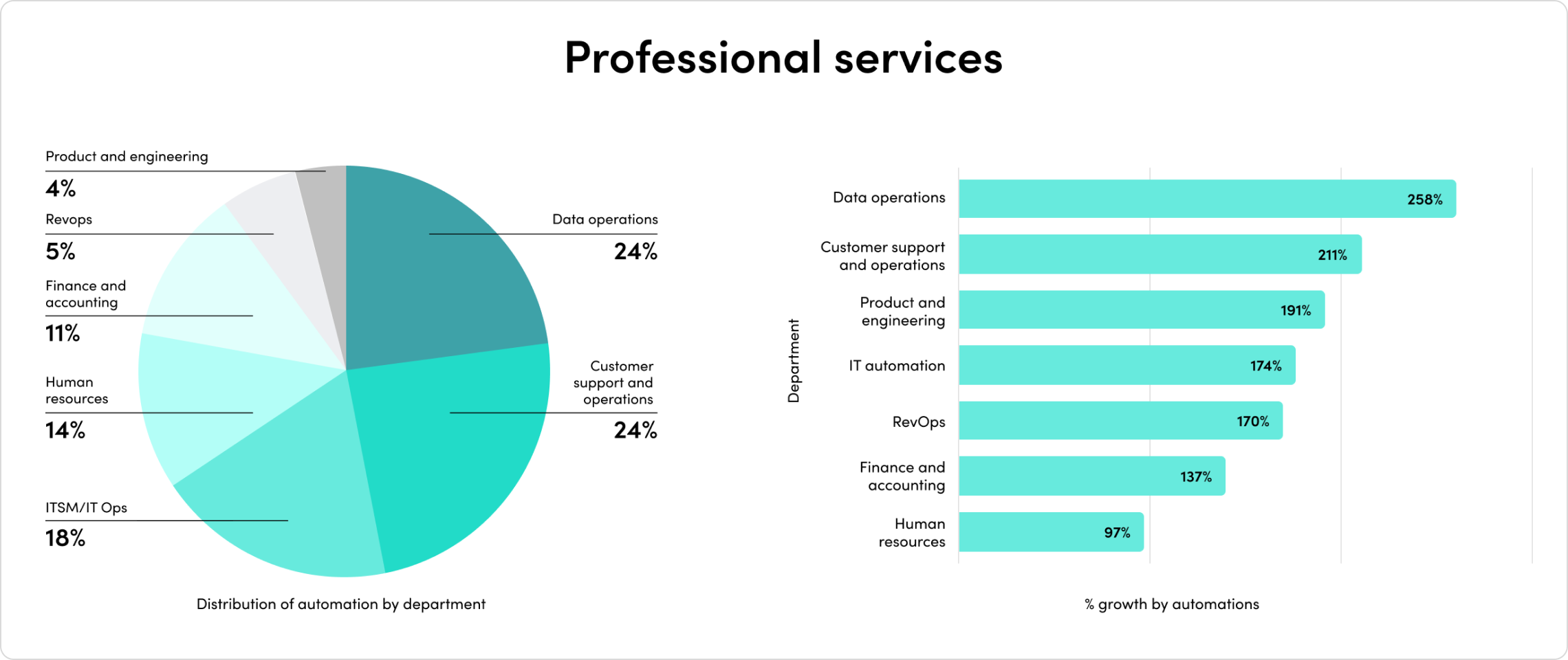
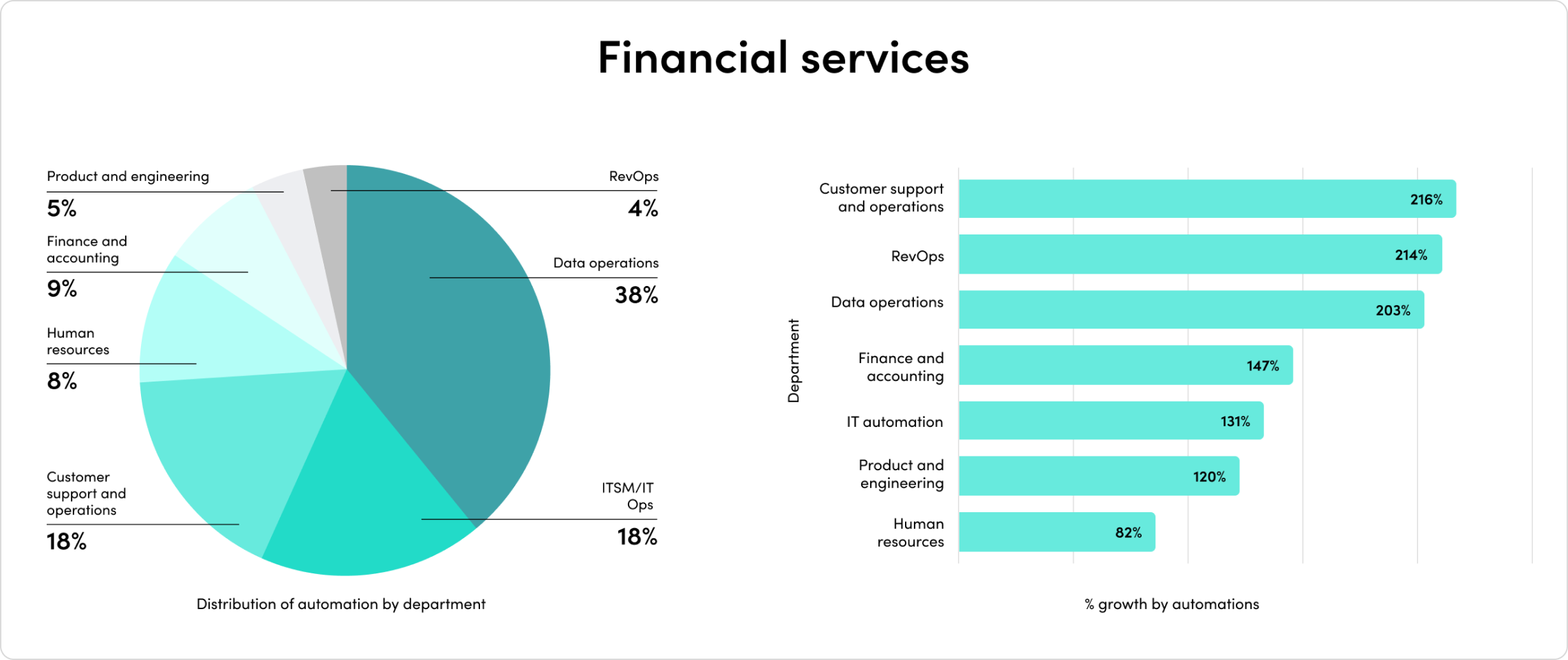
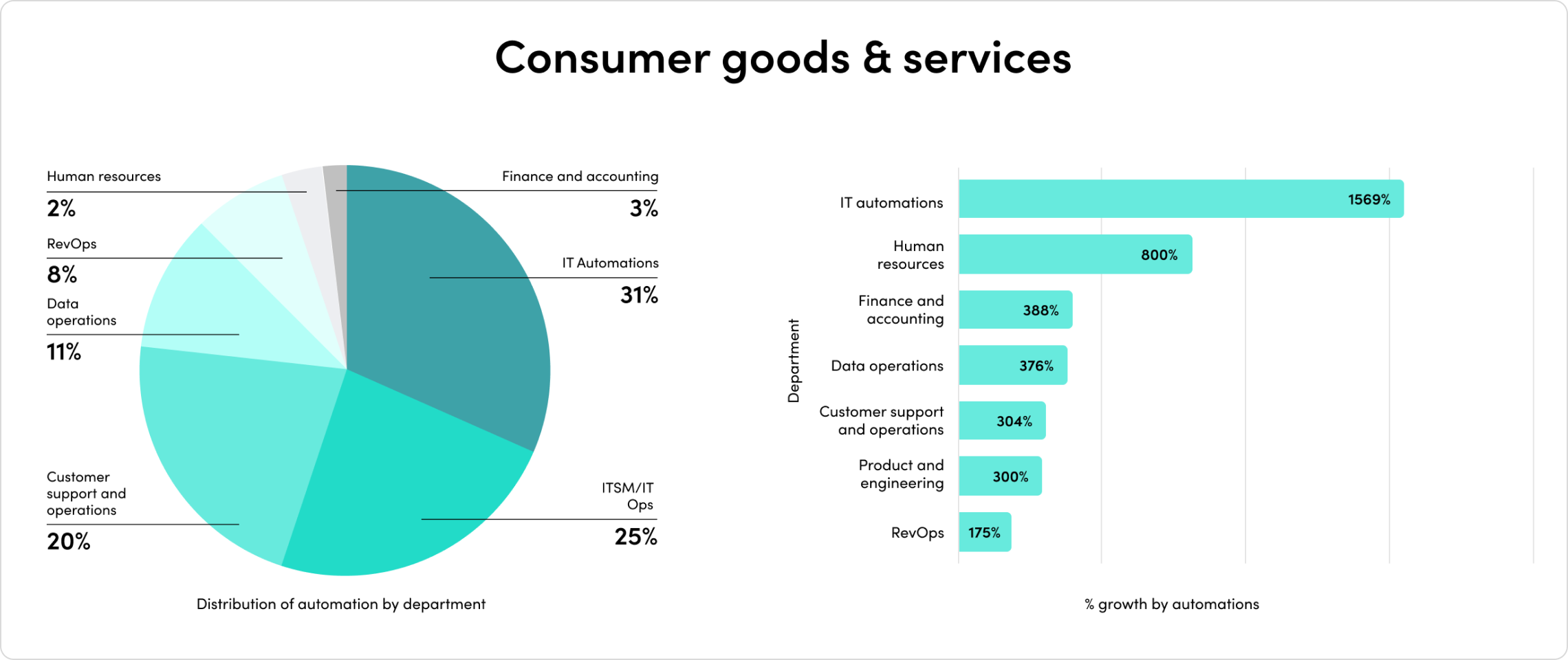
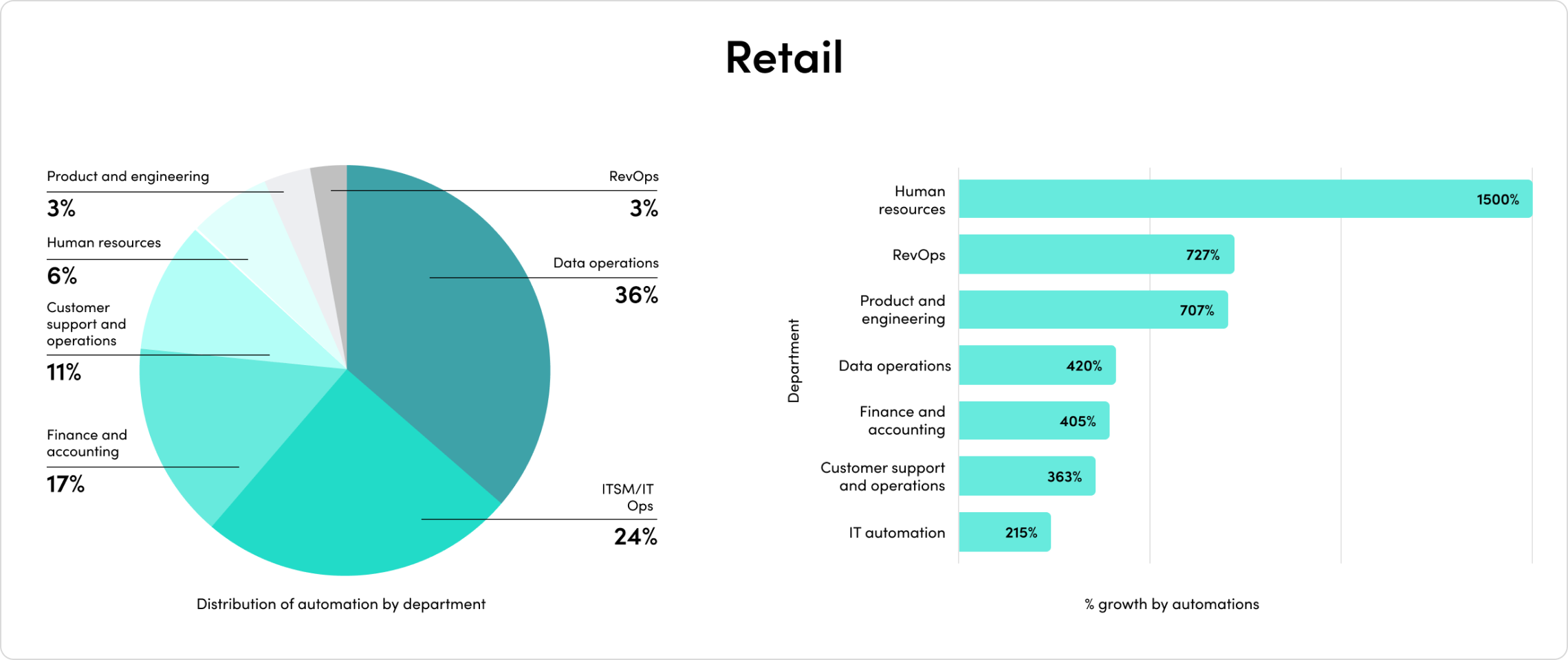
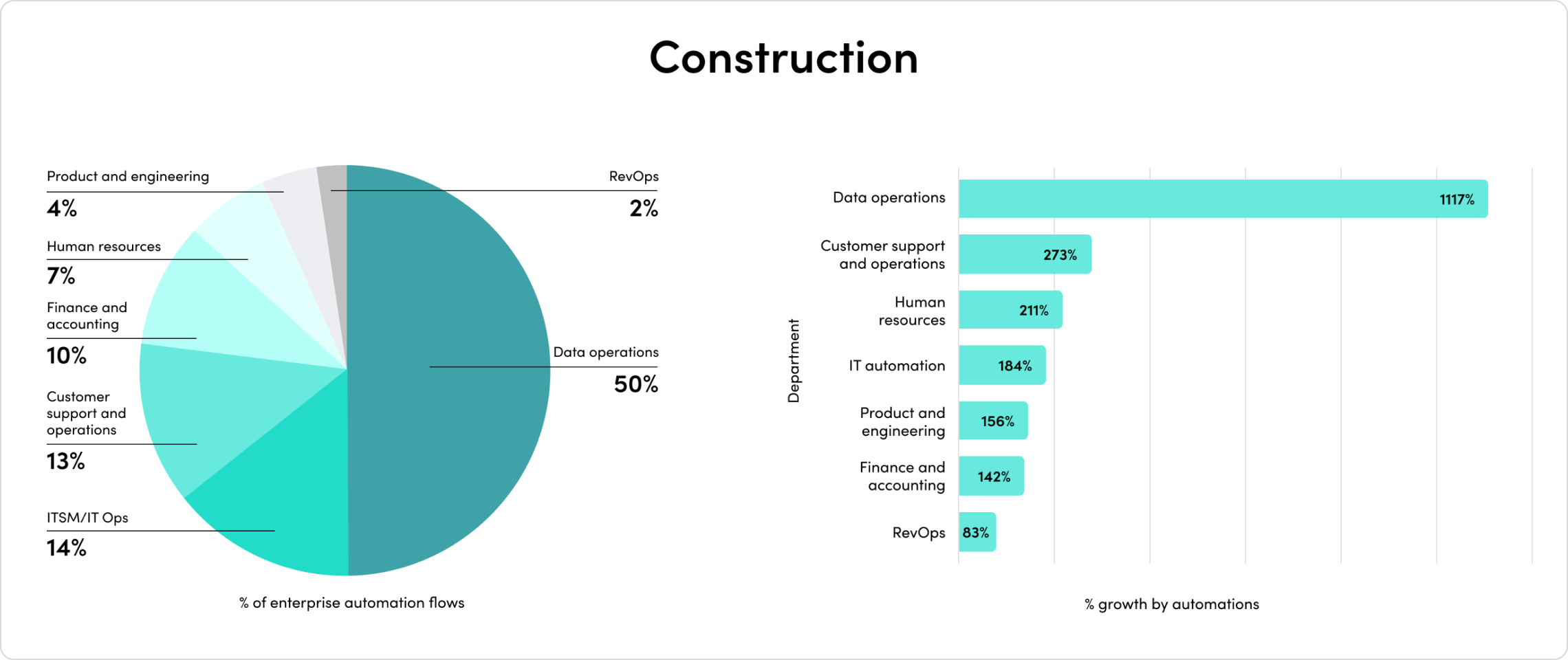
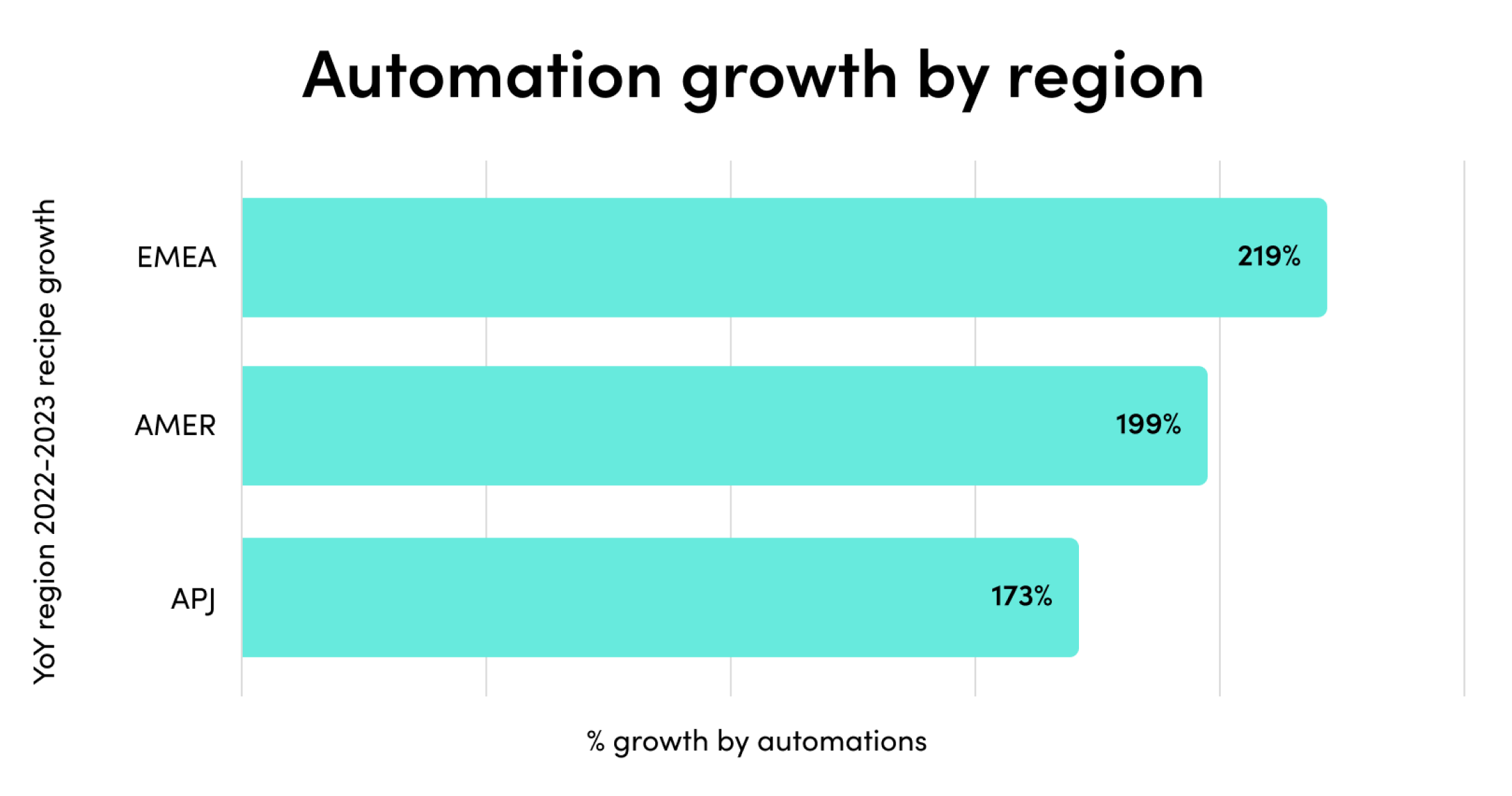
2023’s mix of economic headwinds and AI momentum set the stage for another year of change. Companies are rapidly adopting AI, and their investments are paying off. Automated processes with generative AI have exploded by 500% in the last year alone.
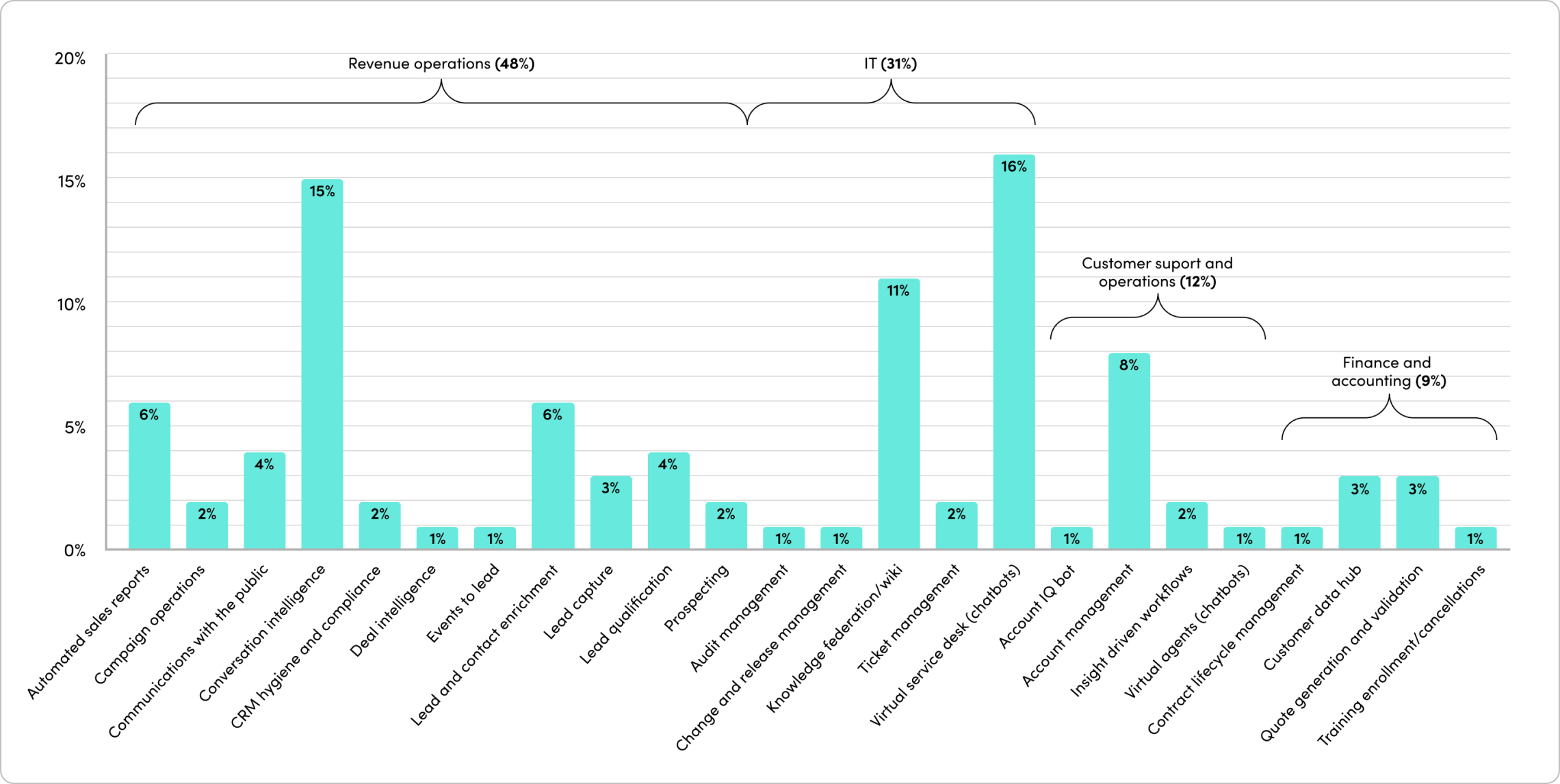
The outcomes have been staggering. Companies report exponential outcomes across team productivity, demand generation, security, customer experience, and more.
The data shows companies are drawing on a mix of new technologies and a new mindset:
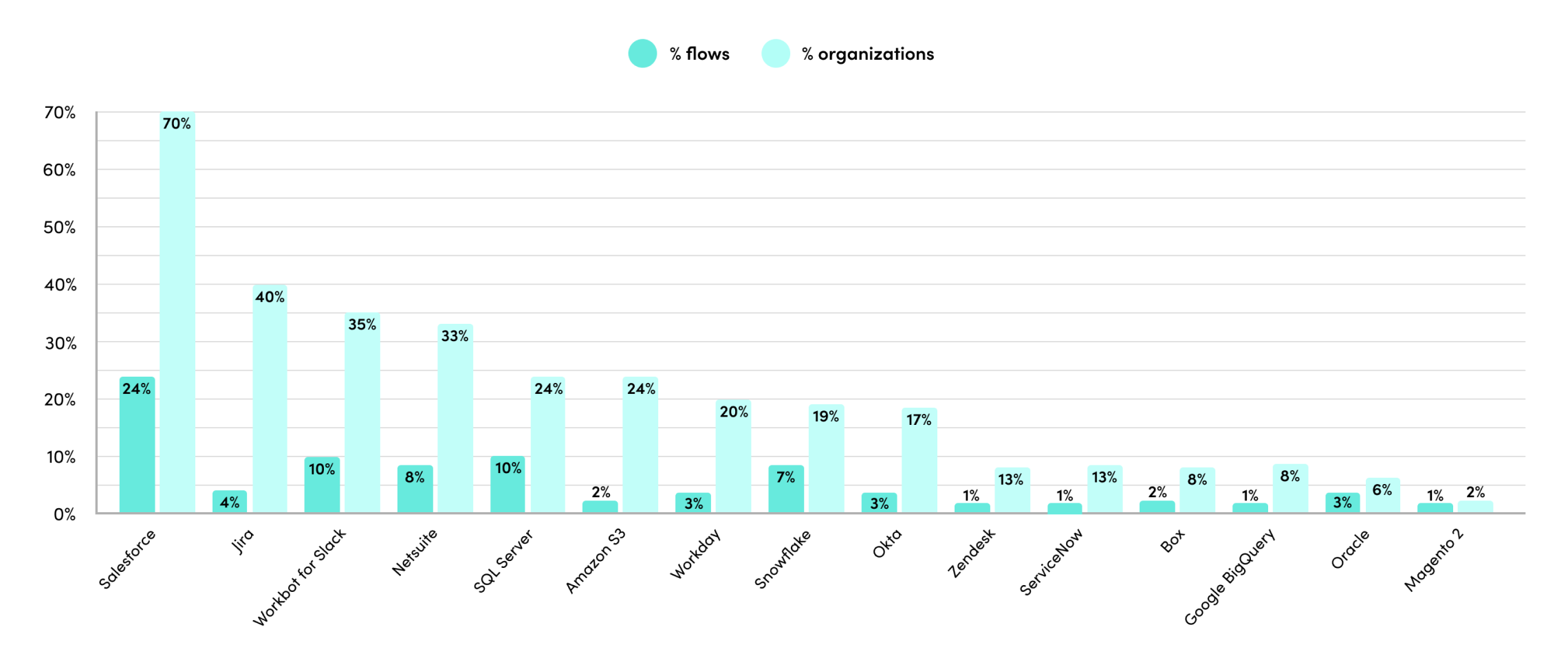
- AI and low-code automation are emerging natural partners in businesses. Their combined forces in businesses are interweaving digital brains (LLMs) throughout business processes.
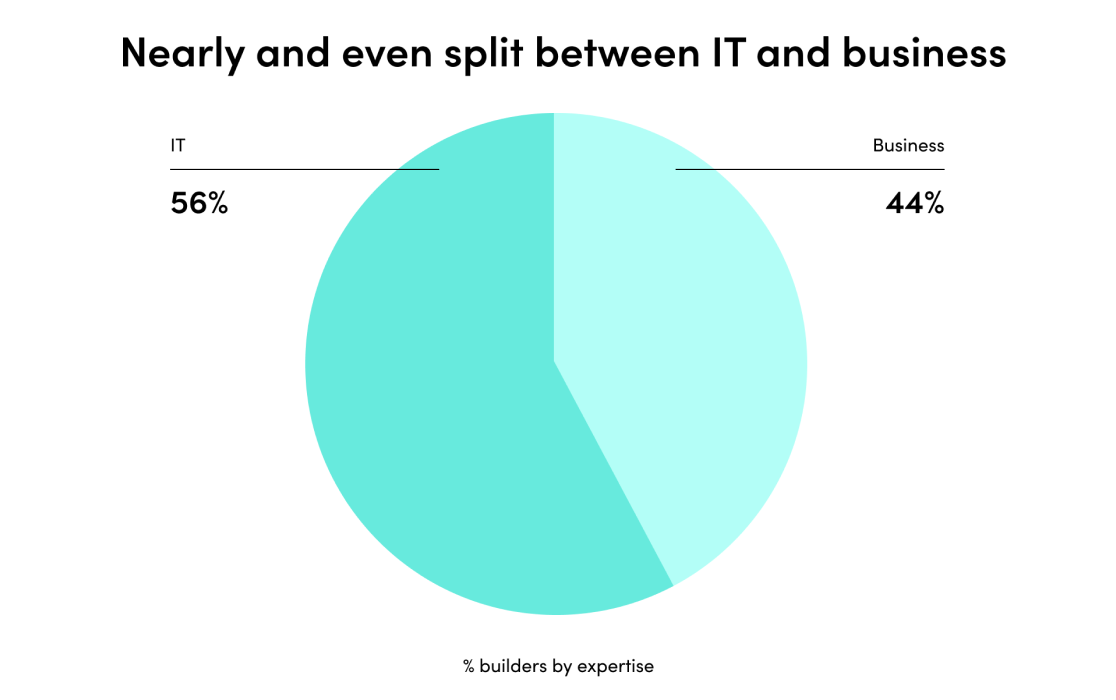
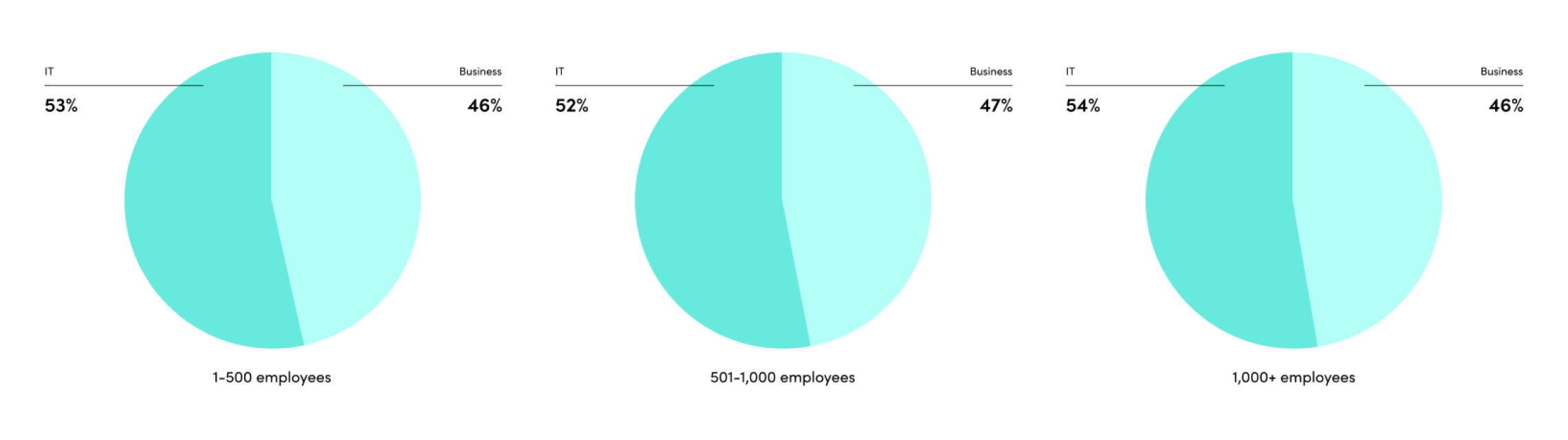
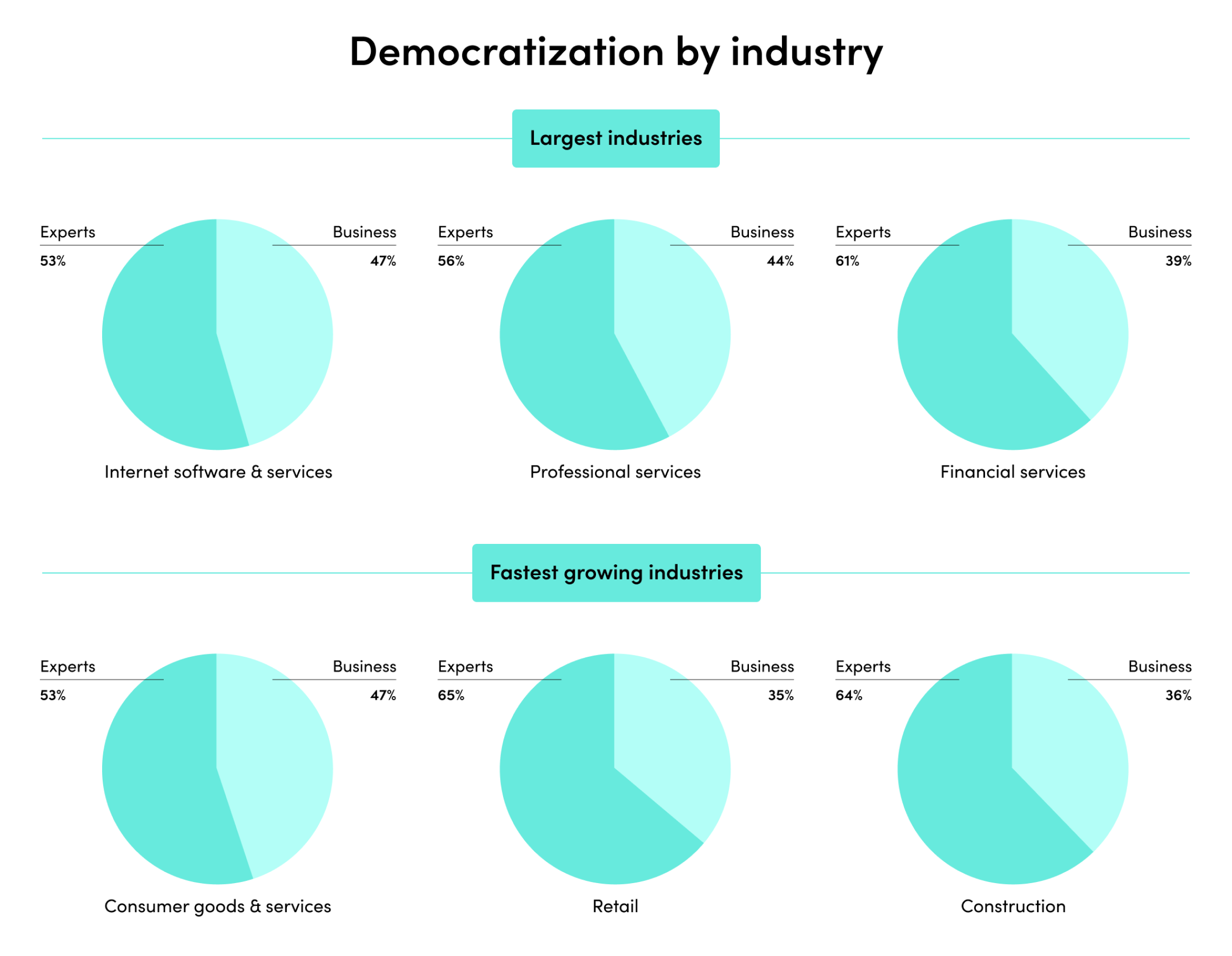
- A new automation mindset that embraces agility, systems thinking, and inclusiveness is on the rise.
In this report, we share real data on how organizations are revolutionizing the way they work with AI, automation, and integration, and what that means for their work in 2024.
This data is based on real, anonymized automated process data collected in 2023. For more detail on the methodology behind this research, see Appendix 3.