In today’s fast-paced digital workplace, Slack acts as a central nervous system for countless teams. It’s where projects are discussed, decisions are made, and information is shared.
But what if your AI agents could tap into this wealth of context to become powerful collaborators? That’s the promise of Model Context Protocol, also known as MCP.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through how to integrate Slack with AI so you can deploy agents trained on your company’s collaboration data.
For developers and automation architects, this integration enables use cases such as automated project summaries, AI-powered internal support, and context-aware agentic workflows, all while maintaining strict security and governance.
Let’s get started!
What is MCP, and Why Connect it with Slack?
Model Context Protocol (MCP) is a specification for exchanging context, capabilities, and structured actions between clients and servers. A server exposes actions and resources, and the client requests actions and receives structured results. This arrangement reduces fragile and brittle connections between assistants and enterprise systems.
(For a broader introduction to MCP, go here.)
Slack is a high-value surface for MCP because conversation threads contain context that agents can learn from and act on. When a Slack MCP client is in place, agents can retrieve thread context, call a ticketing system, post structured updates, and log actions consistently.
This moves you from manual, copy-and-paste interactions to seamless agentic workflows where your AI agents can proactively manage and act on information.
When you connect Slack with an MCP server, it acts as a client and listens for user requests from channels or threads, converts those requests into MCP actions, and then forwards them to an MCP server. The server executes the action and returns text results.
Slack then formats the returned data and posts it directly into the conversation. This arrangement keeps logic centralized on the server and presentation local to Slack.

Things You Need Before Starting
To follow this guide, make sure that you have the following:
- Admin access to Slack Workspace. You will need permission to create and install apps.
- An AI platform that supports MCP. This could be Claude, Cline, or any compatible client.
- The Slack MCP server. You can build it manually, use any existing open source project, or work with an enterprise-ready platform like Workato’s Agentic MCP.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Integrating MCP Server with Slack
Now that we have the prerequisites out of the way, we’ll walk through the process of creating a Slack App, configuring the MCP server, and connecting it to your AI agent.
Creating and Configuring a Slack App
The first step is to create a dedicated app in Slack that will act as the identity for your AI agent.
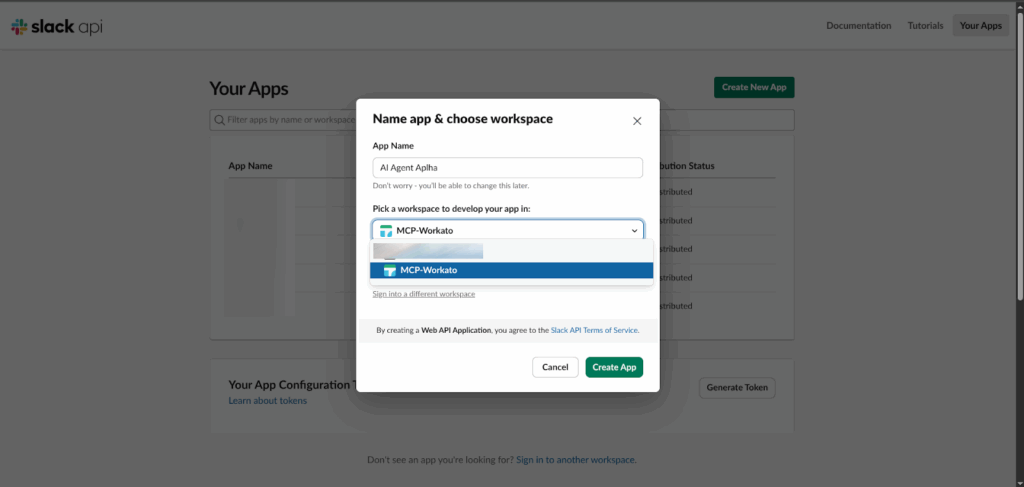
Go to api.slack.com/apps and click “Create New App.” Choose the “From the Scratch” option, name your AI agent (e.g., AI Agent Alpha), and select the workplace you want to connect it to.
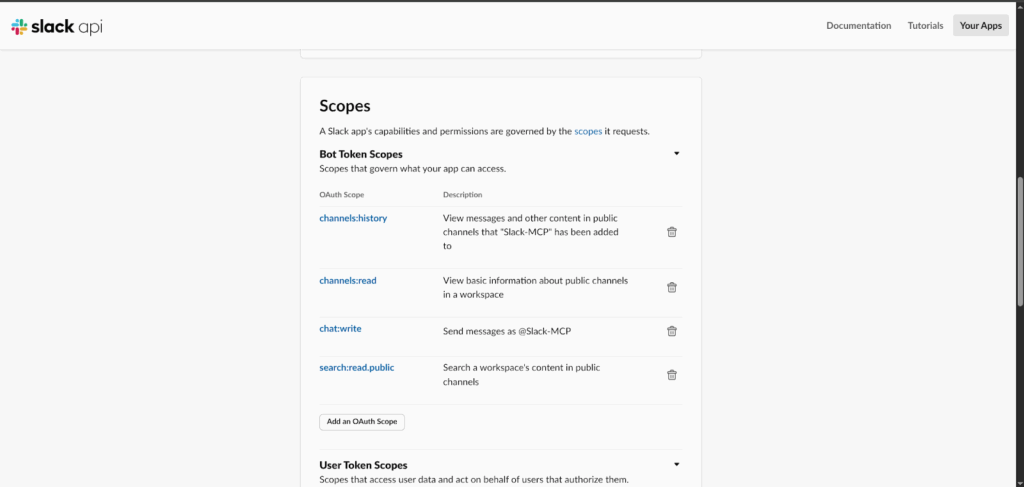
Under OAuth and Permissions, you need to assign Bot Token Scopes. This scope defines what your AI agent can do. For a basic setup, add the following scopes:
- channels:history – to read public channel messages
- channels:read – to list public channels
- chat:write – to send messages as a bot
- search:read.public – to search through conversations
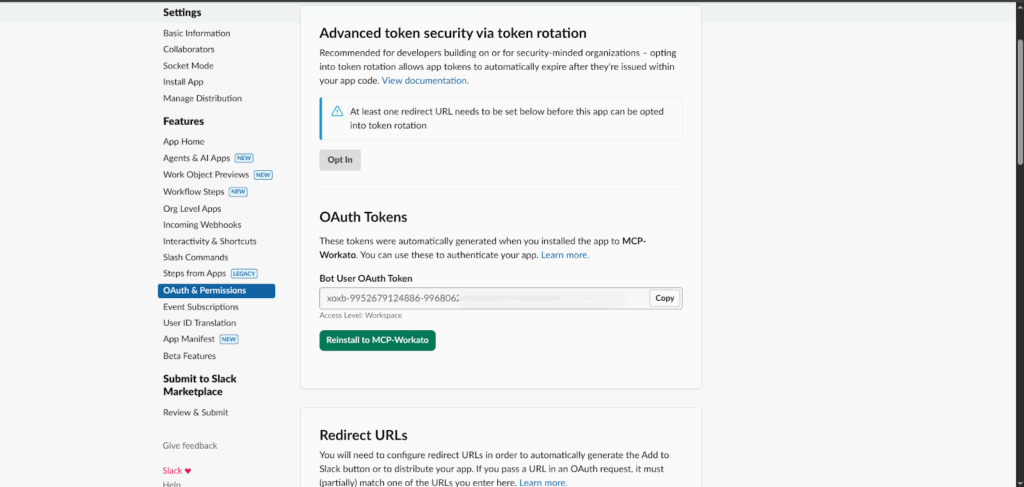
Install the app to your workplace by clicking “Install to Workplace” on the same OAuth and Permissions page. After installation, you’ll be granted a Bot User OAuth token that starts with xoxb. This token is the key your MCP server will use to authenticate.
Installing and Configuring the MCP Server
Now, let’s set up the server that will translate between MCP and the Slack API.
To install the server, you can use Node.js via this command:
npm install -g @your-slack-mcp-package/server
Replace the name of the package with the actual package name. You can also create a custom server using Express and the MCP SDK.
Once you have installed packages, set the environment variable as your server needs the Slack token to connect.
export SLACK_BOT_TOKEN=xoxb-your-copied-token-here
After installation is complete, verify whether everything is working properly by running the server. It should indicate that it is running and waiting for a connection from your MCP client.
Connecting to Your AI Agent
The final step is to tell your AI client about your new Slack MCP server. The exact method for connecting will vary based on the particular client you’re using. For many clients, however, you’ll need to edit a configuration file.
For example, in Claude Desktop, you would edit the claude_desktop_config.json file:
“.json
{
“mcpServers”: {
“slack”: {
“command”: “npx”,
“args”: [
“-y”,
“@your-slack-mcp-package/server”
]
}
}
}
“
After saving the config file and restarting the AI client, it should establish a connection. You can verify this by asking your client a simple question: “What Channels are you able to see in Slack?”
Slack MCP in Action: Key Use Cases and Features
Once connected, your AI agent can perform a number of different actions based on the token scope you’ve defined. Here are some of the ways you can use your agents even if you’re just defining a narrow scope as we did earlier.
Read Channel History and Context
Ask your agent, “Can you summarize the key points from the #project-alpha channel last week?” The AI will use the MCP connection to fetch and process that history.
Send and Manage Messages
Instruct your AI to “Send a message to #alerts saying the deployment was successful.” This automates notifications directly from your workflows, keeping teams informed and aligned.
Search Through Conversations
“Search Slack for any discussions about the Q3 roadmap.” The agent can find and cite relevant conversations across the workspace.
Apart from these use cases, Slack MCP is most useful when paired with multiple MCP servers. To make the most out of the tech, companies also connect Slack to:
- Internal configuration tools
- CI systems
- Ticketing platforms
- Design tools
- Knowledge repositories
Using this approach, Slack becomes the single point of entry into these systems. Rather than building separate chatbots, you can rely on MCP servers with consistent capabilities.
Security and Governance Best Practices
Using internal tools like Slack with AI requires proper governance. Let’s take a look at a few best practices that teams maintain reliable and secure Slack MCP deployments.
- Principle of Least Privilege
Only grant your agentic the privileges it needs to work. If it only reads and ingests the data in certain channels, only give the read permission. This limits the blast radius of a potential misconfiguration.
- Token Management
Never hard-code your Slack bot token in your configurations. Always use environment variables, secure secret manager, or both.
- Maintain a Test Workspace
Always validate the new capabilities in a sandbox environment before enabling them in production. This prevents bugs in production and also reduces noise in operational channels.
- Audit and Monitor
Regularly review the activity logs of your Slack app to see and document the actions your AI agent is performing.
Slack provides request logs for slash commands, event subscriptions, and errors, which help you understand how often AI responds, where requests originate, and whether any unexpected traffic appears.
For a deeper dive into building secure and governable AI integrations, check out our resources on MCP security and governance.

Wrapping Up
While a DIY MCP server is a great start, managing security, scalability, and updates for production can become quite complex.
This is where a unified platform like Workato helps.
By providing an enterprise-ready Slack MCP server as part of its Agentic MCP offering, Workato eliminates the need for manual setup and maintenance and provides pre-built integration for dozens of enterprise systems — like Salesforce, Jira, and Snowflake.
This allows your AI agent to operate across your entire tech stack, all with out-of-the-box security and centralized governance.
To learn more about how to unlock the power of MCP, read A Guide to Workato Enterprise MCP: Secure, Scalable Agentic Integration for the Enterprise.
This post was written by Talha Khalid. Talha is a full-stack developer and data scientist who loves to make the cold and hard topics exciting and easy to understand.